Image source: Shutterstock/PLRANG ART Artur Furmanek
News • Target cells, medication effects, evasion methods
4 new facts about early Covid-19 infections
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers studied SARS-CoV-2 infections at individual cellular levels and made four major discoveries about the virus, including one that validates the effectiveness of remdesivir – an FDA-approved antiviral drug – as a form of treatment for severe Covid-19 disease.
“Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, the way that each individual responds differently to the infection has been closely studied. In our new study, we examined variations in the way individual cells reacted differently to the coronavirus and responded to antiviral treatment,” said Ryan Langlois, PhD, senior author of the study, associate professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology and member of the Center for Immunology at the U of M Medical School. The study was published in the journal PLOS Pathogens.
Source: Fiege et al, PLOS Pathogens 2021 (image provided by University of Minnesota Medical School)
The researchers found that:
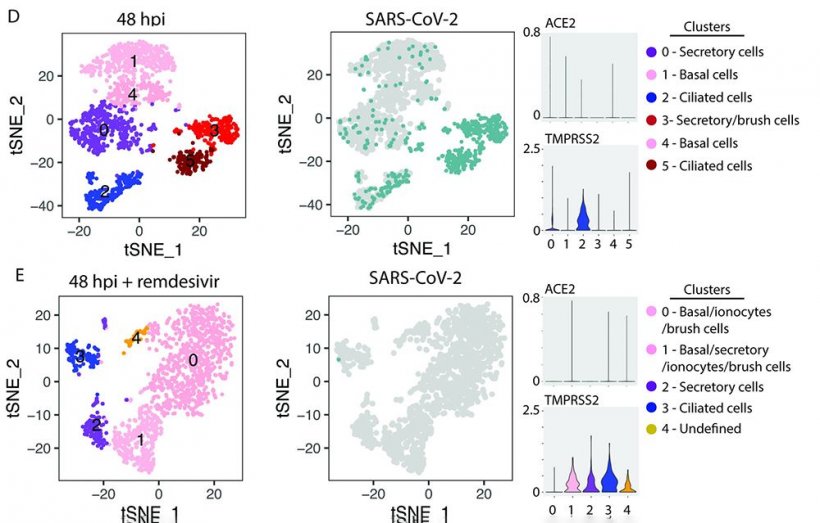
- SARS-CoV-2 primarily infects two types of cells in the upper respiratory tract – ciliated cells and goblet cells;
- Goblet cells are the main producer of pro-inflammatory responses, which are common in severe Covid-19 cases;
- Remdesivir, however, is effective in blocking virus replication in all cell types in the upper respiratory tract;
- SARS-CoV-2 is highly effective at evading initial detection by the innate immune system, but when detected, virus replication is efficiently blunted by antiviral responses.
“Understanding early events in virus-host interactions is critical for understanding the pathophysiology of the disease as well as for identifying appropriate antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs,” Langlois said. “Our results show that ciliated airway epithelial cells are the predominant cell type initially infected by SARS-CoV-2, and importantly, that remdesivir is capable of reducing viral replication in all infected cell types within this culture system.”
Recommended article

News • COVID-19 gateway
Nose cells identified as likely coronavirus entry points
Two specific cell types in the nose have been identified as likely initial infection points for COVID-19 coronavirus. Scientists discovered that goblet and ciliated cells in the nose have high levels of the entry proteins that the COVID-19 virus uses to get into our cells. The identification of these cells by researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, University Medical Centre Groningen,…
The diverse population of cells lining the human airway, called “airway epithelium,” is the very first line of defense against Covid-19 and can set the stage for immune responses that either protect against disease or cause damage. Using a cutting-edge technique that comprehensively measures reactions by single cells, Langlois’ team discovered that SARS-CoV-2 is capable of infecting most cell types in the human airway and identified a key gene required for viral entry. “As expected, we observed a large amount of variation between different cells in the antiviral immune response, paving the way for future studies that will better characterize why some individuals are relatively protected against severe Covid-19 disease,” Langlois said.
Source: University of Minnesota Medical School
12.02.2021