Image source: Adobe Stock/Juan Gärtner
News • MS biomarker
Blood marker gives new insights into multiple sclerosis
Nerve damage in multiple sclerosis (MS) can be detected via the concentration of neurofilament light chain in the blood. According to researchers from the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel, this neuron-specific protein provides valuable information on future disease course and the effectiveness of therapies.
MS is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that leads to transient or permanent functional impairment of functions of the nervous system and eventually increasing disability. However, the disease can worsen very differently from person to person, making it difficult to detect disease activity early and accurately and hence tailor treatment to individual needs. Researchers led by Professor Jens Kuhle have now described the importance of the protein neurofilament light chain (NfL), which occurs exclusively in nerve cells, as a valuable and specific marker for nerve damage in MS. They have reported their findings in the journal Lancet Neurology.
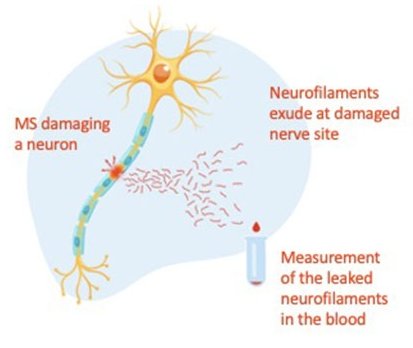
Image source: University of Basel, University Hospital Basel
For their study, the researchers determined NfL concentrations in more than 20,000 blood samples from over 10,000 patients with MS and healthy control persons (see box). They were able to assess the effects of aging and body weight on normal concentrations measured in healthy control persons, and thereby to determine more precisely determine the threshold to pathologically elevated levels in patients. They used the data to create a large, international reference database that enabled them to identify increased values of NfL in individual blood samples of patients with MS in a meaningful way, indicative of ongoing disease activity. This method also allowed the team to better compare the efficacy of different MS therapies.
In two large independent groups of people with MS, a strong correlation was found between elevated levels of NfL in the blood and current disease activity in the central nervous system. Strikingly, the researchers, using this precise method, also detected elevated NfL levels in a group of MS sufferers in whom the disease did not appear to be active according to conventional and standard of care criteria. “Even if the condition of those affected appears to be stable with the clinical and imaging methods available today, the damage to the nervous system appears to progress insidiously and initially unnoticed in some cases,” explains Dr. Pascal Benkert, who shares first authorship of the study with PhD student Stephanie Meier.
In addition, the Clinical Neuroimmunology Research Group, which is based in the Departments of Clinical Research and Biomedicine, shows that this blood marker also allows certain predictions to be made: patients with high NfL concentrations in the blood thus have an increased risk of future MS disease activity. They are more likely to experience inflammatory episodes or a deterioration in their health.
The results of the study show that this blood marker allows for more accurate assessments of disease activity compared with the methods used previously. “The results offer hope that it will be possible to more precisely chose and tailor therapy to individual disease courses,” says study leader Kuhle. “This is an important step towards individualized MS therapy that is tailored to the patient.”
Source: University of Basel
18.02.2022





