Article • Digital pathology and AI
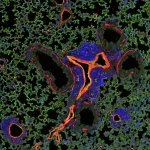
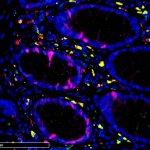
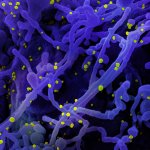
Finding new biomarkers to match the biological complexity of cancer
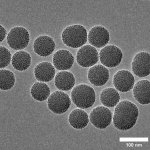
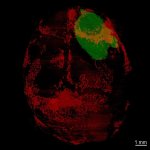
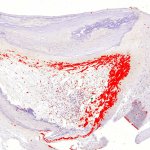
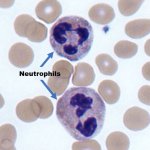
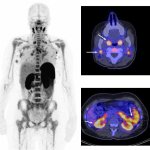
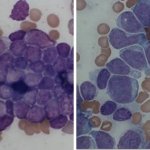
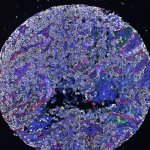
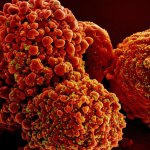
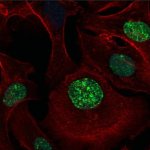
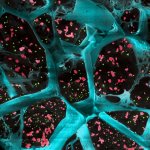
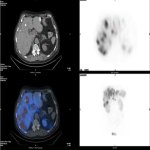
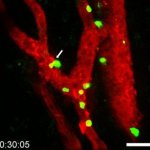
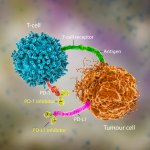
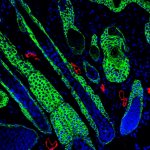
Advances in artificial intelligence and multimodal data integration are poised to revolutionise cancer diagnostics – but significant challenges remain before these technologies can be routinely deployed in clinical practice. Professor Manuel Salto-Tellez outlined the steps needed to bridge the gap between complex tumour biology and the relatively simple biomarkers currently available, speaking…