News • Flexible electronics implant
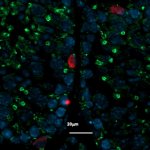
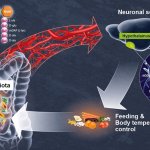
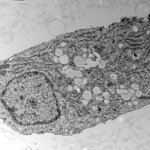
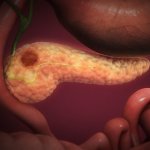
“Cyborg” transplant could fix diabetes damage to the pancreas
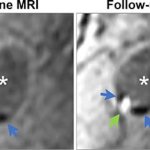
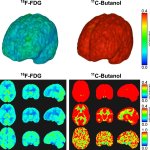
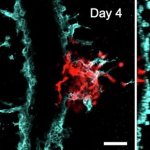
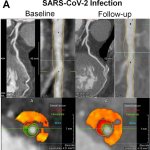
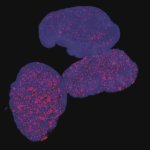
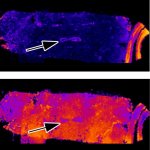
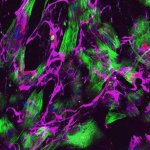
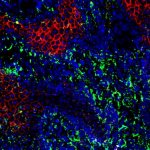
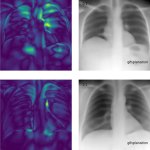
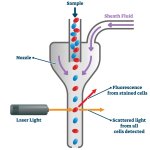
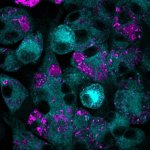
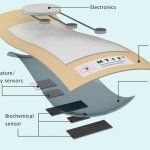
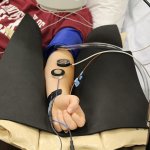
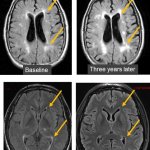
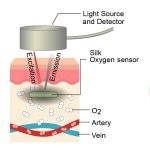
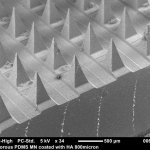
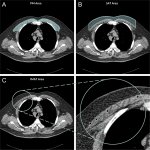
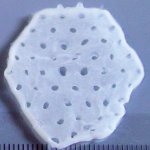
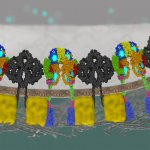
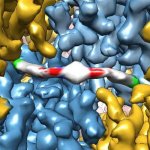
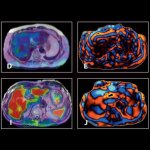
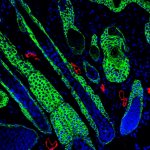
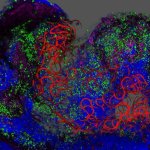
Researchers have created a ‘cyborg’ pancreas device - an ultrathin mesh of conductive wires within growing pancreatic tissue - that could open up new ways for treating diabetes.