News • Radiology research
Chest CT illuminates COPD mortality risk
Body composition information derived from routine chest CTs can provide important information on the overall health of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including their risk of all-cause mortality.
This is the result of a new study, published in Radiology. COPD is a group of chronic, progressive lung diseases that affect about 30 million people in the United States alone. It is frequently associated with obesity and sarcopenia. Obesity is associated with lower mortality in patients with COPD. The longer survival rates of obese patients compared to leaner counterparts, a phenomenon known as the “obesity paradox,” has been suggested in several chronic illnesses.
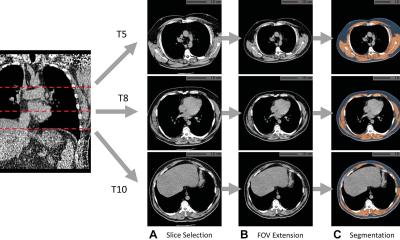
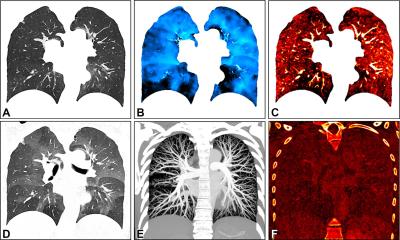
Chest CT is often used to characterize COPD, screen for lung cancer, or plan for surgical options. Beyond lung assessment, these exams offer an opportunity to assess obesity and sarcopenia through soft-tissue biomarkers. “Chest CT scans have long focused on the lungs or heart,” said study coauthor and Radiology editor David A. Bluemke, MD, PhD, from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison. “Few prior investigators have evaluated muscle quality, bone density, or degeneration of the spine as an index of overall health. These are readily available and quantifiable in these CT examinations.”
Recommended article

News • Cardiac health
Too good to be true? New study challenges ‘obesity paradox’
The idea that it might be possible to be overweight or obese but not at increased risk of heart disease, otherwise known as the “obesity paradox”, has been challenged by a study of nearly 300,000 people published in in the European Heart Journal.
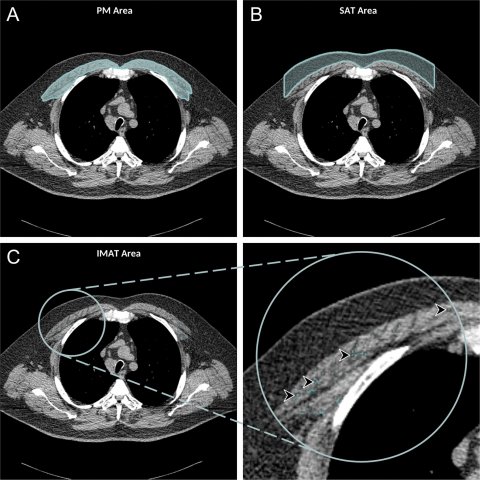
For the new study, Dr. Bluemke, along with Farhad Pishgar, MD, MPH, and Shadpour Demehri, MD, from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and colleagues used chest CT exams to study the associations between imaging-derived soft tissue markers and all-cause mortality in COPD. The study group was made up of 2,994 participants drawn from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), a large trial investigating the roles of imaging-derived soft-tissue and bone markers for predicting outcomes relevant to cardiopulmonary diseases. Of the 265 patients in the study group with COPD, 49 (18%) died over the follow-up period. A greater amount of intermuscular fat was associated with higher mortality rates. Existing research has linked higher levels of intermuscular fat with diabetes and insulin resistance. Higher subcutaneous adipose tissue, in contrast, was linked to lower risks of all-cause mortality.
I expect that more studies in the future will begin looking at all information on the CT, rather than just one organ at a time. Clinicians will need thresholds when to intervene when fat or bone abnormalities become severe
David A. Bluemke
The authors convincingly showed fat in the muscle was much more predictive of bad outcomes than a simple distribution of subcutaneous fat. The findings point to a role for body composition assessment in people with COPD who undergo chest CT. Such assessments are readily obtainable in clinical practice. In theory, CT-derived body composition assessments would provide an opportunity for earlier interventions in patients who face a higher risk of adverse health events.
Body composition assessments taken from chest CT also present an opportunity for artificial intelligence-derived algorithms that could quickly and automatically add risk assessment to the imaging report. “I expect that more studies in the future will begin looking at all information on the CT, rather than just one organ at a time,” Dr. Bluemke said. “Clinicians will need thresholds when to intervene when fat or bone abnormalities become severe.”
The study was just the latest to tap into imaging data from the MESA trial, a collaboration involving more than 6,000 men and women from six communities across the United States.
Source: Radiological Society of North America
07.04.2021