Article • Imaging in tandem
MRE plus Fib-4 jointly detect liver fibrosis
Rather than using techniques separately, researchers have determined that coupling image-based and serum-based biomarkers achieves a higher diagnostic accuracy in detecting stage two liver fibrosis, or above.
Report: Mark Nicholls
The study team, from the NAFLD Research Center, University of California at San Diego (UCSD), and colleagues at Yokohama City University in Japan, used magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) in tandem with the serum-based Fib-4 clinical prediction rule. Their aim was to decide whether MRE alone, or combined with Fib-4, may be used for non-invasive identification of candidates for pharmacologic therapy among well-characterised patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Their findings were presented virtually at the Digital International Liver Congress 2020 at the end of August by Jinho Jung of the UCSD NAFLD Research Center.

NAFLD is estimated to have a global prevalence of 25% and NAFLD patients with stage two fibrosis, or higher, have a significantly increased risk of progression to cirrhosis and liver-related mortality. The gold standard for determining whether a patient is a candidate for pharmacologic therapy is liver biopsy, but this has limitations in terms of variability and discomfort.
Given the global burden of NAFLD, Jung said that liver biopsy assessment to decide candidacy for treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) related fibrosis is impractical. ‘Therefore,’ he added, ‘there is an unmet need in the pathologic testing arena to accurately identify each fibrosis patient in a non-invasive manner with a high positive predictive value.’
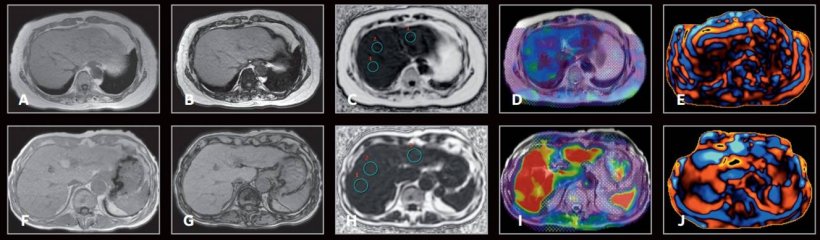
There are currently some non-invasive diagnostic tests for detection of liver fibrosis, with image-based biomarkers such as Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE), Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography (VCTE), Sheer Wave Elastography (SWE) and Acoustic Force Radiation Impulse (ARFI). In addition, serum-based biomarkers include Fibrosis 4 (Fib-4), NAFLD Fibrosis score, Enhanced Liver Fibrosis score (ELF) and Fibrospect II. A combination of two unrelated biomarkers, such as image-based and serum-based biomarkers, has been proposed for staging of liver fibrosis and within the context of NAFLD, promising results have been shown to detect patients with advanced fibrosis or stage three fibrosis or higher.
Limited data
However, there are limited data on whether this data or clinical prediction rule can be applied to stage two fibrosis or higher patients and its cut points. To explore this, the – ‘Utility of magnetic resonance elastography in accurate identification of candidates for pharmacologic treatment of NASH related fibrosis: a prospective cohort study’ – aimed to examine whether MRE alone, or in combination of Fib-4, may be used for non-invasive identification of candidates for pharmacologic therapy among well characterised patients with NAFLD with liver biopsy assessment using NASH CRN histologic scoring system as the reference standard.
Findings, which underlined the value of MRE in this context, were validated in a geographically and ethnically diverse external independent validation cohort with collaborators in Yokohama.
The UCSD cohort of 238 patients with a range of ethnicities had 170 with stage 0-1 and 68 had fibrosis stage two or higher. The validation cohort in Japan recruited 222 patients with stage 0-1 and 138 fibrosis stage two or higher. Jung said: ‘We found that MRE is more accurate than routinely available current prediction rule Fib-4 in detecting stage two fibrosis or above. The difference was clinically and statistically significant.’
Positive predictive value

Combining MRE with FIB-4 (MRE≥3.3kPa and FIB-4≥1.6) to develop a clinical prediction rule to rule in ≥stage two fibrosis patients showed a positive predictive value (PPV) of 97.1% in the UCSD-NAFLD cohort, and remained significant at 91.0% in the Japan-NAFLD cohort. It is important to note that the cut-points were determined through UCSD-NAFLD cohort and then were validated in the Japan-NAFLD cohort. ‘By coupling MRE and Fib-4 we could achieve higher diagnostic accuracy compared to MRE and Fib-4 alone,’ said Jung. ‘With the cohort being geographically and ethnically diverse, this stresses the clinical applicability of these results in a western and eastern population.’
He acknowledged that there are caveats and limitations to the findings and the findings are only recommended for usage in hepatology clinic settings to rule in patients for pharmacologic treatments. ‘As cut points may be different in primary care settings,’ he said, ‘further study needs to be done in a primary care or diabetes clinic.’
Jung concluded that this study – led by Professor Rohit Loomba, Director, NAFLD Research Center – will serve as a clinical prediction rule to give a high positive corrective value for clinicians to rule in patients to reduce the burden of patients for avoidable risk of liver biopsy.
Profiles:
Jinho Jung is a researcher at the University of California, at San Diego NAFLD Research Center, with specific interests in various aspects of NAFLD, including non-invasive imaging, biomarkers and clinical trial design.
Rohit Loomba is Director of the NAFLD Research Center and leader of the study.
01.12.2020