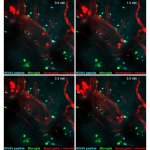
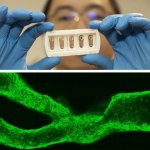
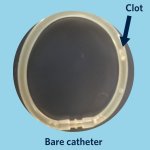
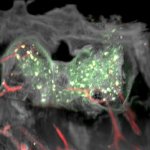
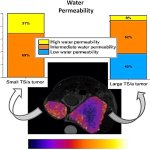
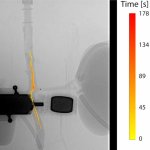
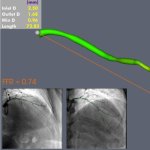
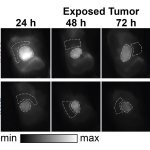
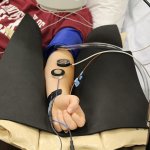
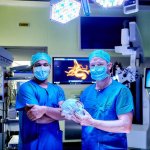
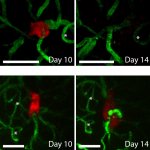
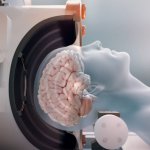
News • Lymphovenous bypass
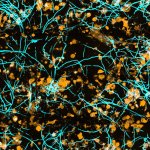
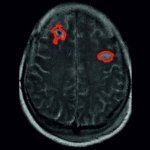
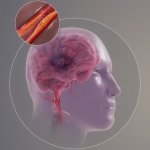
A surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
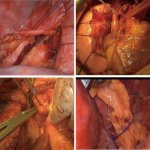
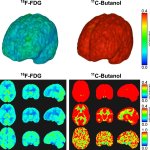
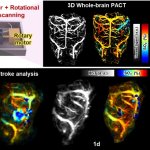
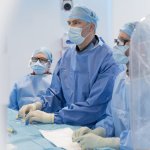
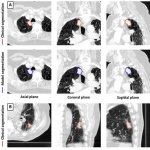
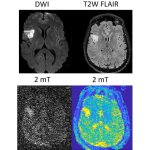
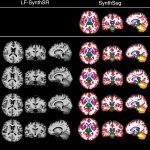
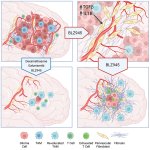
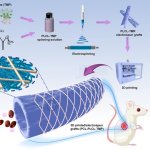
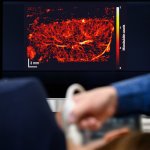
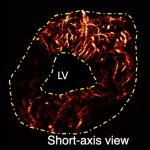
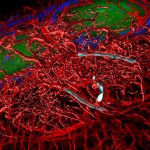
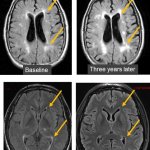
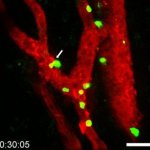
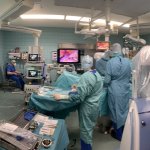
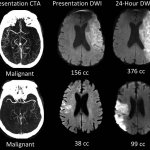
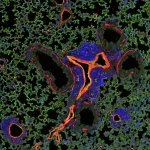
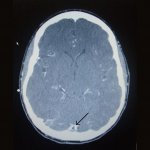
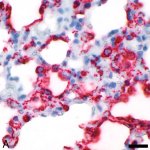
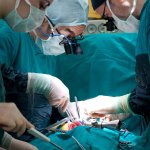
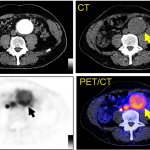
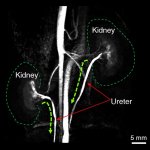
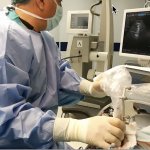
A small but growing body of evidence suggests that a minimally invasive surgical procedure called lymphovenous anastomosis (LVA) might be an effective treatment for Alzheimer's disease.