News • 3D microprinted scope
World’s smallest imaging device focuses on heart disease
A team of researchers led by the University of Adelaide and University of Stuttgart has used 3D micro-printing to develop the world’s smallest, flexible scope for looking inside blood vessels.
The camera-like imaging device can be inserted into blood vessels to provide high quality 3D images to help scientists better understand the causes of heart attack and heart disease progression, and could lead to improved treatment and prevention.
In a study published in the journal Light: Science & Applications, a multidisciplinary team of researchers and clinicians was able to 3D print a tiny lens on to the end of an optical fibre, the thickness of a human hair.
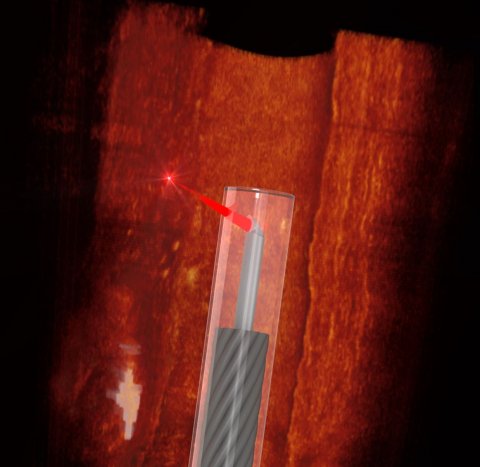
Photo by Simon Thiele and Jiawen Li
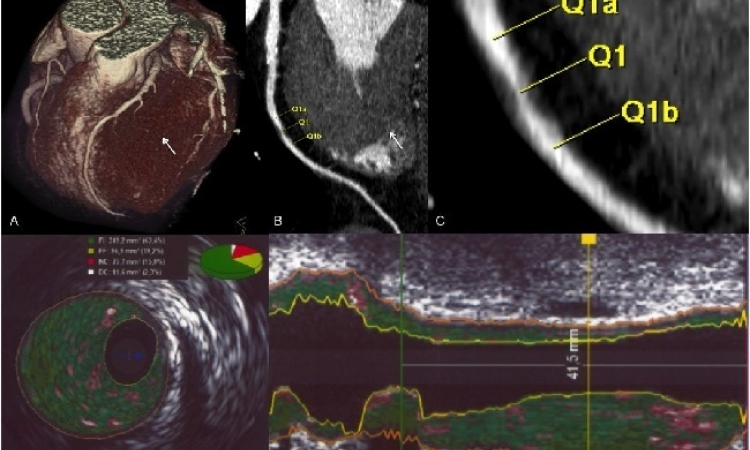
The imaging device is so small that researchers were able to scan inside the blood vessels of mice. Dr Jiawen Li, co-author and Heart Foundation Postdoctoral Fellow at the Institute for Photonics and Advanced Sensing, University of Adelaide, says in Australia cardiovascular disease kills one person every 19 minutes. “A major factor in heart disease is the plaques, made up of fats, cholesterol and other substances that build up in the vessel walls,” Dr Li said. “Preclinical and clinical diagnostics increasingly rely on visualising the structure of the blood vessels to better understand the disease. Miniaturised endoscopes, which act like tiny cameras, allow doctors to see how these plaques form and explore new ways to treat them.”
Dr Simon Thiele, Group Leader, Optical Design and Simulation at the University of Stuttgart, was responsible for fabricating the tiny lens. “Until now, we couldn’t make high quality endoscopes this small,” Dr Thiele said. “Using 3D micro-printing, we are able to print complicated lenses that are too small to see with the naked eye. The entire endoscope, with a protective plastic casing, is less than half a millimetre across.”
Dr Li explains: “It’s exciting to work on a project where we take these innovations and build them into something so useful. It’s amazing what we can do when we put engineers and medical clinicians together.”
The research collaboration also included researchers from The South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute, The Royal Adelaide Hospital and Monash University.
Source: University of Adelaide
22.07.2020