Adapted from: Manjua et al., Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 2021 (CC BY 4.0)
News • Angiogenesis
Magnetic stimulation boosts blood vessel formation
Magnetic fields can be used to stimulate blood vessel growth, according to a new study.
The findings, published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials by researchers at the Técnico Lisboa and NOVA School of Science and Technology in Portugal, could lead to new treatments for cancers and help regenerate tissues that have lost their blood supply. “Researchers have found it challenging to develop functional, vascularized tissue that can be implanted or used to regenerate damaged blood vessels,” says Frederico Ferreira, a bioengineer at Técnico Lisboa’s Institute for Biosciences and Bioengineering. “We developed a promising cell therapy alternative that can non-invasively stimulate blood vessel formation or regeneration through the application of an external low-intensity magnetic field.”
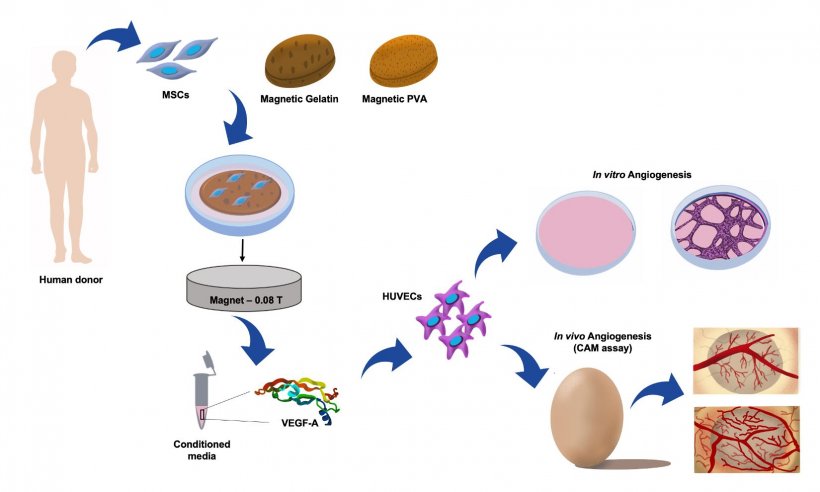
Image source: Manjua et al., Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 2021 (CC BY 4.0)
The researchers worked with human mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow. These cells can change into different cell types, and also secrete a protein called VEGF-A that stimulates blood vessel formation. Ana Carina Manjua and Carla Portugal, at the Research Centre LAQV at the NOVA School of Science and Technology, developed two hydrogel supports, made from polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) or gelatin, both containing iron oxide nanoparticles. Cells were cultured on the hydrogels and exposed to a low-intensity magnetic field for 24 hours.
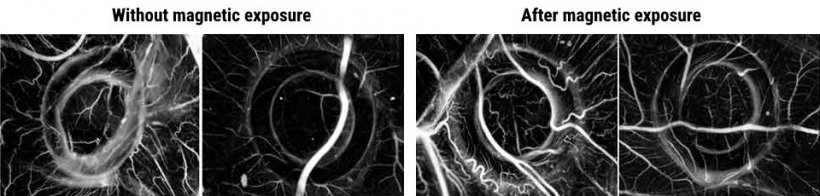
The cells on the PVA hydrogel produced less VEGF-A after the magnetic treatment. But the cells on the gelatin hydrogel produced more. Subsequent lab tests showed that this VEGF-A rich extracts, taken from the cultures on magnet-stimulated gelatin hydrogel, improved the ability of human vascular endothelial cells to sprout into branching blood vessel networks. Endothelial cells were then placed onto a culture dish with a gap separating them. The conditioned media from magnet-treated mesenchymal stromal cells from the gelatin hydrogel were added to the endothelial cells, moving to close the gap between them in 20 hours. This was significantly faster than the 30 hours they needed when they had not received magnetic treatment. Placing a magnet directly below the dish triggered the mesenchymal stromal cells to close the gap in just four hours. Finally, VEGF-A extracts produced by magnet-treated mesenchymal stromal cells on gelatin increased blood vessel formation in a chick embryo, although further research is needed to confirm these results.
More work is needed to understand what happens at the molecular level when a magnetic field is applied to the cells. But the researchers say gelatin hydrogels containing iron oxide nanoparticles and mesenchymal stromal cells could one day be applied to damaged blood vessels and then exposed to a short magnetic treatment to heal them. The team suggests that magnet-treated cells on PVA, which produce less of the growth factor, could be used to slow down blood vessel growth to limit the expansion of cancer cells.
Source: Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
22.07.2021