Article • From ablation to neuromodulation
The new era of functional radiosurgery
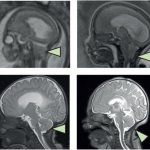
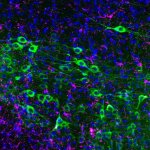
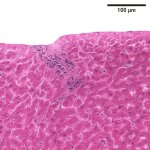
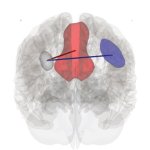
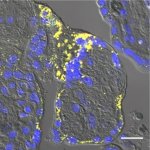
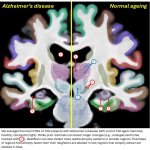
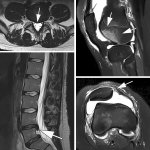
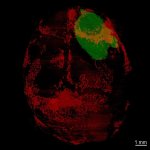
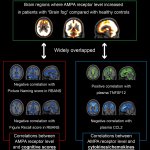
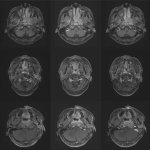
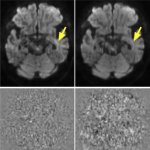
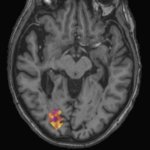
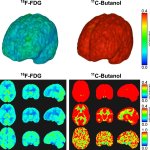
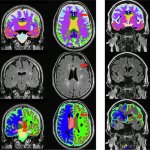
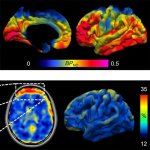
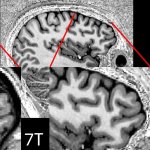
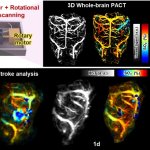
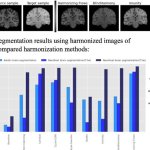
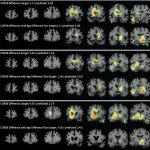
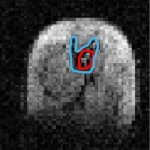
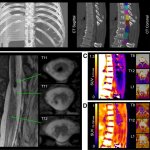
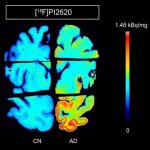
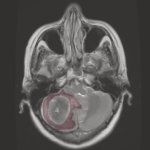
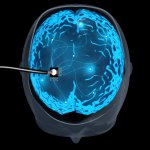
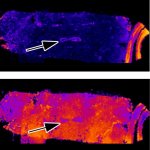
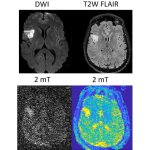
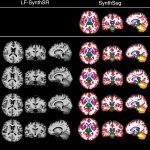
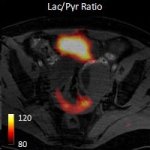
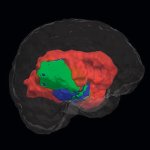
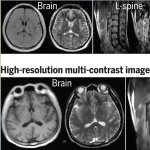
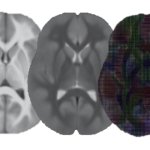
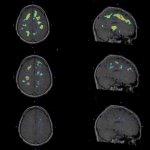
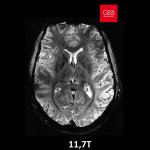
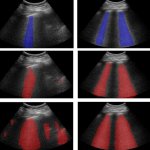
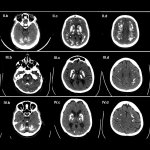
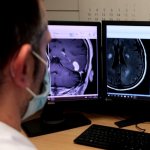
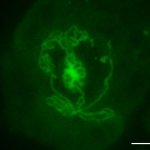
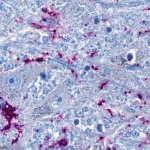
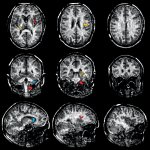
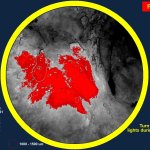
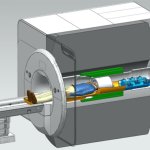
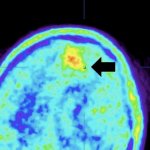
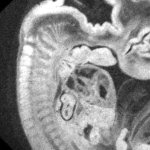
Functional brain radiosurgery is an application of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), representing its newest clinical field. It is a precise, non-invasive medical technique using focused ionising radiation to precisely target specific brain structures to modulate brain function for neurological disorders, psychiatric conditions, or intractable pain. The technology offers “precision without…