News • Plasmid-specific ecological adaptation
How antimicrobial resistance spreads from gut bacteria to hospital superbugs
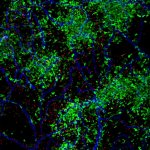
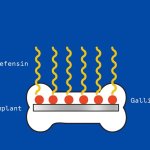
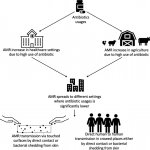
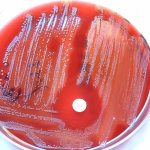
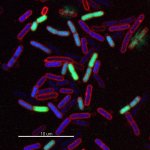
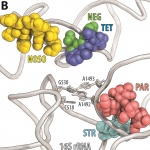
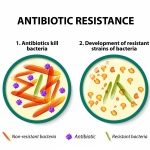
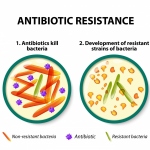
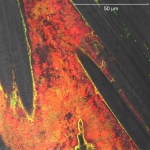
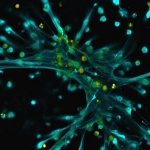
Researchers have uncovered how a high-risk class of genetic vectors can efficiently spread antibiotic resistance within the gut, enabling even highly virulent bacteria to acquire drug resistance.