
News • Assessing infection risk
Predicting neonatal sepsis with vaginal microbial swabs
A new study shows that analyzing bacteria from vaginal swab samples taken at delivery could help predict the risk of neonatal sepsis.

A new study shows that analyzing bacteria from vaginal swab samples taken at delivery could help predict the risk of neonatal sepsis.

Researchers have uncovered how a high-risk class of genetic vectors can efficiently spread antibiotic resistance within the gut, enabling even highly virulent bacteria to acquire drug resistance.

Should younger and older people receive different treatments for the same infection? New research suggests that age-specific treatments may be necessary in ongoing antibiotic resistance crisis.

Gene-editing technologies show great promise for medical treatments and research, with the potential to cure thousands of genetic diseases. At the 2025 World Medical Innovation Forum in Boston, leading experts explored the possibilities and challenges of these rapidly advancing tools. The case of Baby KJ Muldoon – an infant treated with a personalised CRISPR therapy developed in just seven…
With antimicrobial resistance causing over 5 million deaths annually, rapid outbreak detection is critical. A German lab demonstrates how FTIR spectroscopy can transform hospital infection control.

Now, a research team has developed a novel diagnostic approach that enables the rapid and simultaneous detection of both antibiotic resistance and high virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae.

New research shows that a harmless strain of Klebsiella – discovered by chance in laboratory experiments – can eliminate infections and reduce gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Researchers from Osaka have developed a simple and efficient system for understanding the functions of specific norovirus genes, providing new avenues for developing antivirals and vaccines.

Climate change, poverty, and drug resistance are combining to create an escalating health crisis that could become a ‘creeping catastrophe’ if left unaddressed, a new international study finds.
New insights into the intestinal nervous system – or "gut brain" – open new avenues for advancing therapies for allergies, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome.

Microplastics pose a human health risk in more ways than one, a new study reveals: not only do the particles harbor pathogenic bacteria, they may also help the spread of antimicrobial resistance.

Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a hospital-acquired bacterium that causes serious infections, can move from the lungs to the gut inside the same patient, raising the risk of sepsis, new research reveals.

A team of researchers comprehensively catalogued a new collection of bacteria-eating viruses called phages. These phages could be used to combat Klebsiella pneumoniae - a serious threat in hospitals.
Scientists are on the way to finding a vaccine to fight off Helicobacter pylori - a bacterium found in over 60% of people - possibly preventing stomach ulcers and lowering the risk for stomach cancer.

Integrating liquid metal nanomaterials into a ceramic scaffold could improve the durability and biocompatibility of orthopedic implants, while also combatting antimicrobial resistance.
When the many protect the few: An expert explains the premise of herd immunity, and how vaccinations apply the priciple in preventing communicable diseases, notably in the complete eradication of smallpox.

Scientists created precise replicas of Candida sugar coats to understand immune responses, enabling fast bedside testing that could replace slow lab cultures.

Climate change enables mosquito-borne pathogens such as the chikungunya and West Nile virus to establish themselves in Europe. ECDC experts explain how EU countries can adapt to this ‘new normal’.

The mere fact of being exposed to a sick avatar in a virtual reality environment triggers a measurable immune response in humans, a multidisciplinary research team discovered.

When should preventive mastectomy be offered for women at higher risk of breast cancer? A new evaluation model defines thresholds at which risk reducing surgery should be recommended.

Antibiotics are known for disrupting the microbiome in the gut and thus paving the way for diseases. However, many common non-antibiotics also have this effect, a new study shows.

When someone is infected with a virus, traces of it are shed in their bodily waste and end up in the sewage system. Thus, combined wastewater and individual testing can benefit public health response.
New research shows how embryos can protect themselves from bacterial infections even before forming their immune system. The findings could provide new insights into the origin of immunity.

Microbiota composition can help prevent pathogenic bacteria from proliferating, known as the barrier effect. Now, scientists have identified seven bacteria involved, paving the way for new therapies.
A University of Liverpool study has used advanced genetic and genomic techniques to offer a major step forward in understanding and diagnosing infectious intestinal diseases.
A US research team has shown that Sars-CoV-2 can “reprogram” pathogen-fighting white blood cells into immune system suppressing cells — a potential mechanism by which severe Covid may arise.

The rise of pathogenic fungi is a real concern and is being driven by climate change. A new study predicts significant spread of certain fungal pathogens in Europe fuelled by rising temperatures.

Researchers incorporated a specialized breath sensor within the fabric of a face mask to detect metabolites associated with chronic kidney disease. Initial tests showed promising results.

Finding ways to target antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a scientific and medical priority. A consortium of researchers identified a compound capable of blocking a key protein for virulence, thus “disarming” the pathogenic bacteria.
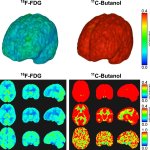
Using an advanced PET scanner, US radiologists explore how cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and other systemic conditions, can affect the brain by assessing the impact on the blood-brain barrier.

Researchers discovered a key mechanism by which melanomas and other aggressive tumours prevent the immune system from detecting and attacking them – one of the greatest challenges in oncology today.
World TB Day raises awareness about tuberculosis and commemorates the discovery of the source bacterium M. tuberculosis. More than a century later, scientists still refine anti-TB strategies.
Europe has been polio-free since 2002 – but a recent surge in poliovirus detections across several European countries shows that the threat from this vastly-forgotten disease is over, warn experts.

More than just a sports injury: A new study shows that head trauma may activate latent viruses, leading to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.

A new way to inhibit the proliferation of Sars-CoV-2 opens up new perspectives in the fight against this coronavirus and other viral diseases that still have no medical treatment.

The current rise in antibiotic resistance is once again sparking interest in phage therapy. Now, scientists developed a new tool that recommends the best possible phage cocktail for a given patient.
Two studies indicate warning signs about spread of bacteria resistant to the same group of antibiotics (carbapenems) in both healthcare and community settings across Europe.

Wastewater treatment fails to kill several human pathogens, such as Listeria or E. coli, when they hide out on microplastics in the water, according to a new study.
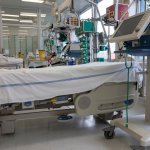
UK scientists are harnessing the power of AI to assess the antimicrobial resistance of patients in intensive care units (ICUs) and identify sepsis-causing bloodstream infections.
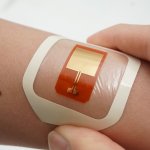
Rsearchers developed a novel bioelectronic device that taps into the natural electrical activity of certain bacteria found on our skin, paving the way for a drug-free approach to managing infections.

The gut microbiome varies from person to person in terms of the bacterial species represented and their colonization density. Segatella copri is the most prominent germ. Researchers at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research goal to clarify its health significance.

While awareness for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in bacteria is relatively high, fungal pathogens remain largely ignored – a blind spot with potentially dire consequences for global health.
Protection from established Covid-19 vaccines wanes relatively quickly. A new vector vaccine elicits prolonged immune response in animal models, and maintains its efficacy over extended time.
Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant (AMR) bacteria are a major issue in hospitals. A new technique aims to effectively track all types of relevant microorganisms simultaneously.
Klebsiella is among the top three pathogens responsible for hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). Now, researchers discovered why the bacteria thrive in clinical environments.

New research reveals a promising approach to developing a universal influenza vaccine that confers lifetime immunity against an evolving virus considered most likely to trigger the next pandemic.

Staphylococcus aureus is a leading cause of hospital-acquired bacterial infection, associated with over one million deaths worldwide each year. Now, researchers could be one step closer to a vaccine.
How do pathogenic bacteria evolve to become epidemic? To find out, researchers examined DNA data from almost 10,000 samples taken from infected individuals, animals, and environments around the world.

Integrating bacterial genomic data with detailed human mobility data makes it possible to see how pathogens causing pneumonia and meningitis, move between regions and evolve over time.

A new study describes the outcome of a new approach to testing for Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) guided by the principles of diagnostic stewardship, to help rein in the overtreatment of patients.

Researchers have succeeded in developing “pathoblockers” that provide protection against the most common pneumonia-inducing pathogens, even if they are resistant to antibiotics.

A new approach to vaccine development could produce vaccines before the disease-causing pathogen – such as a new variant of the coronavirus Sars-CoV-2 – even emerges.

Could the 'gene scissors' CRISPR be used to make resistant bacteria susceptible to first-line antibiotics again? According to new reseach, yes – but the experts also point out serious caveats.

Antimicrobial-resistant infections have become a global threat, with an annual death toll of over 1 million. Now, reseachers created a promising vaccine candidate for antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The world has hardly processed Covid-19, so the thought of another pandemic is far from pleasant. Yet, infectious disease experts have picked the most likely candidate in a new survey.

A new study identifies hospital sinks as a source of bacterial outbreaks, highlighting the vulnerability for contamination. The researchers also point out the difficulties in stopping such outbreaks.

Bacteria can help – or hinder – the treatment of cancer. How this happens, however, is largely unknown. Now, researchers have mapped bacteria in cancer metastases to shed more light on their role.
Researchers are developing novel active substances designed to cut off the nutrient supply of resistant bacteria, effectively starving them to death.
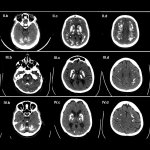
Much like joints or blood vessels, the brain can be affected by calcifications. This can lead to neurodegenerative disease, but is not well studied. Now, researchers from Norway identified a gene that provides new insights.

An international study has revealed that MRI monitoring in women with mutations in the BRCA1 genes significantly reduces breast cancer mortality without the need for preventive mastectomy.

Why are we doing what we are doing to stop surgical infections? A new research review in the run-up to the ECCMID congress 2024 will look at improving preventive measures.
A new guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cryptococcosis is designed to support medical staff in handling invasive fungal infections and provide guidance and support in decision-making.

Once a patient’s body has been colonized by resistant bacteria, they can persist for a long time, a new study by the University and University Hospital of Basel shows.

Instead of killing viruses and bacteria with chemical disinfection, a new approach uses minuscule spikes to skewer them. This could be used to prevent surface contamination in hospitals or labs.

Three disease subtypes, based on causes rather than symptoms: A new classification model for Parkinson's disease aims to pave the way for better diagnostics and therapies.

Researchers have analysed the rise of antibiotic resistance over the last 20 years in the UK and Norway, highlighting that antibiotic use is not the only factor in the increase.
A new synthetic antibiotic developed by University of Liverpool researchers is shown to be more effective than established drugs against ‘superbugs’ such as MRSA, a new study shows.
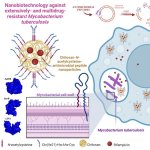
A low-cost technology involving nano-sized antimicrobial compounds against tuberculosis has been developed by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP).
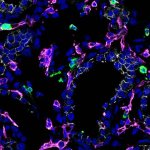
Researchers have created a first-of-its-kind immune cell atlas of the developing lung, revealing coordination between the immune and respiratory systems much earlier than previously thought.

A new approach to the identification of harmful bacteria: A new study explores how spectroscopic techniques can be used for quick analysis directly from the skin.

Breaking & entering – on a minuscule scale: US researchers have shown how some pathogens like Toxoplasma can enter cells using physical force to cause an infection.
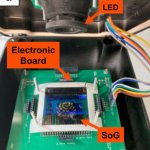
Over the last 20 years, the development of lab-on-a-chip (LoC) devices for performing real-time PCR (LoC-PCR) has been an active research field. Now, Italian researchers present their design for a new lab-on-a-chip-PCR device.

Würzburg resarchers have created a new pseudovirus design that allows tracking of penetration of viruses into cells.

Being able to rely on a quality, safety-engineered device for blood collection allows staff to perform their tasks with the minimum of fuss. Nurse Constance Mak talks about the benefits of closed collection systems.

Environmental changes may reduce the diversity of mosquitos, but bring about a greater abundance of viruses, scientists from Charité in Berlin in cooperation with Leibniz-IZW find.

From cancer to AI, from management to new medication: this year's Labmed Forum at MEDICA 2023 in Düsseldorf (November 13-16) once again features an exciting scientific programme.
A new research breakthrough could lead to the development of new treatments for people with compromised immune systems, such as those with cystic fibrosis.

Brain tumour progression to a malignant state is believed to be the result of an intricate interplay between cancer cells and the tumour microenvironment. Greek researchers shed new light on the mechanisms.
Curbing levels of harmful air pollution could help reduce antibiotic resistance, according to the first in-depth global analysis of possible links between the two.
German bioinformaticians have now detected an unexpected diversity of certain cell appendages in the bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii that are associated with its pathogenicity.
Global warming could hasten the release of ‘time-travelling’ pathogens from melting permafrost and ice that have been trapped for millennia, new research finds.

Under the impulse of the European Commission, the in vitro diagnostic industry is developing emerging technologies to implement sustainable practices in medical laboratories. As sustainability has been a growing priority of the European Union (EU) in the last decade, ‘the medical technology sector, particularly the IVD sector, must comply with European legislation in this field like all other…
Combining aerosol sampling and ultrasensitive biosensing, researchers have created a real-time monitor that can detect any of the Sars-CoV-2 virus variants in a room in about 5 minutes.

A new publication discusses deep-ultraviolet (DUV) photonics for the disinfection of Sars-CoV-2 and its variants (Delta and Omicron) in the cryogenic environment.
Newly developed “smart” coatings for surgical orthopedic implants can monitor strain on the devices to provide early warning of implant failures while killing infection-causing bacteria.
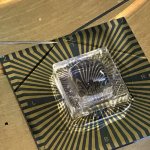
US scientists report using a single-atom-thick nanomaterial to simultaneously detect Covid-19 and flu viruses — at much lower levels and much more quickly than conventional tests for either.
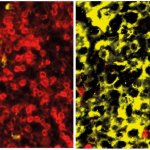
A team of scientists has successfully generated genetically defined mouse models for two subtypes of multiple myeloma. This will contribute to a better understanding of how the disease develops in humans.

Arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures has seen enormous progress in recent years, but complications due to infections are still a major problem. With good preparation and the right technique, however, orthopaedic surgeons can take away much of the horror of this scenario.

The European Football Championship in 2021 had an impact on the participating countries' coronavirus infections, a new study shows. However, the extent depended greatly on the initial situation.

A newly developed rapid test needs only a few seconds to reliably detect pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2. It is based on specially designed magnetic nanoparticles.

Eunsin Bae, M.D. specializes in laboratory medicine and leads the Institute of Clinical Research at Seegene Inc. Her research focuses on microbiology, molecular biology, and hematology. Dr. Bae is currently working toward implementing a global clinical study and establishing an international network of clinical investigations.

Innovative gastrointestinal imaging, medical panel PCs with hygiene optimisation, smartphone-based diagnostic tools, and sustainable hardware setups: At Medica 2022, manufacturers from Taiwan again showed their capability to adapt and provide solutions for a world radically changed by the Covid-19 pandemic. Under the “Taiwan Excellence” banner, outstanding products from the island nation’s…

The diminished power of the immune system in older adults is usually blamed on the aging process. But a new study shows that decades of particulate air pollution also take a toll.
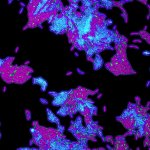
A new Oxford University study provides the first direct evidence of antibiotic resistant bacteria migrating from a patient’s gut microbiome to the lungs, increasing the risk of deadly infections.

Blood stem cell transplantation is a radical but highly effective therapy for multiple sclerosis. A study examined how the treatment curbs the disease and how the immune system regenerates afterwards.

Speed or accuracy? As far as Covid-19 tests go, this was the choice you had to make. In the future, this dilemma could be a thing of the past.

The Pluslife Mini Dock System is a Next-Generation POC molecular diagnostic tool that can be used in different application scenarios, which aims to help the decentralization of MDx in diagnosing facilities.
With the rise of syndrome-style infections, co-infections and the current antimicrobial resistance challenges, the need for multiplexed diagnostics is now more important than ever.
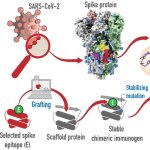
A vaccine design approach that could protect against new variants of SARS-CoV-2 but also potentially protects against other coronaviruses is one step closer to reality as a result of new research.
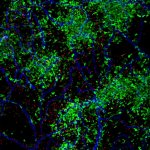
Researchers mapped in detail how the immune system acts against pathogens invading the brain. This sheds new light on host-pathogen interactions and the long-term consequences of brain infections.

What will the next pandemic look like? Health officials from across the globe gathered in Geneva in late August at a World Health Organization meeting to focus on how lessons learned from Covid-19 might best prepare civilization for the "next one."

Researchers at Queen’s University Belfast have developed a new plastic film that can kill viruses that land on its surface with room light.

Dutch global DNA/RNA technology solutions provider MolGen B.V., participates in the 24th Annual Conference of the European Society for Clinical Virology (ESCV) held in Manchester, UK.

German researchers present a novel method for testing chemical agents that could help in the development of drugs against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.

The new washer-disinfector series exhibits comprehensive decontamination and disinfection performance against all human-pathogenic viruses, confirms accredited testing laboratory HygCen Germany GmbH.

A comprehensive assessment of scientific literature has uncovered empirical evidence that more than 58% of human diseases caused by pathogens, such as dengue, hepatitis, pneumonia, malaria, Zika, have been aggravated by climatic hazards.

Cardiomyopathy is not a uniform disease. Rather, individual genetic defects lead to heart failure in different ways, an international consortium reports.

Avian flu, MERS, Covid-19, monkeypox: outbreaks of infectious diseases are getting more common in Europe. As a result, the EU must adapt its surveillance strategies and introduce more data-driven, interdisciplinary countermeasues.

Researchers have identified an enzyme that is a promising new therapeutic target to combat the dangerous bacterial disease melioidosis.

Indwelling catheters through the urethra often cause bacterial infections. A newly discovered synthetic peptide is a promising treatment option, even against antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
A sprayable coating that can prevent the surface spread of infection from bacteria and viruses – including Covid-19 – over a sustained period has been developed by Australian researchers.

The Covid-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of the fast and accurate diagnosis of infectious diseases in clinical settings. Harald Maier discusses the implementation of rapid molecular diagnostics in the central clinical diagnostics laboratory at Innklinikum Altötting and Mühldorf, highlighting how the use of PCR testing has benefitted the hospital during the Covid-19 pandemic.
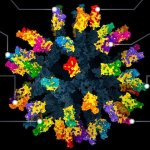
A new type of vaccine provides protection against a variety of SARS-like betacoronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 variants, in mice and monkeys, according to a new study.

Recovery from severe Covid-19 is characterized by a reduction of certain white blood cells and changes in the molecular regulation of the immune system, an international research team found.
Over the last 50 years, malaria parasites have developed resistance to seven drugs, but a new way to identify future antimalarials holds promise.

When a virus makes its way into the body, one of the immune system’s first responders is a set of pathogen-removal cells called macrophages. But they don’t all target viruses in the same way.
Hospital-acquired infections are dangerous for patients and costly for clinics. A novel surface treatment could help improve the safety of medical devices and ease the economic burden.
Bacteriophages – viruses that kill bacteria – could be a solution for fighting antibiotic-resistant pathogens, French researchers have developed a model to better predict their efficacy.

Sofia 2 C. difficile FIA is a new solution to provide reliable and rapid test results with high clinical relevance before empiric therapy decisions are implemented.
Scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology discover new drug target for severe asthma and fibrosis.

The search for rare mutations in bacterial genome could lead to better diagnostics and treatments – reducing morbidity caused by the deadly disease.

Researchers developed a new microfluidic chip with broad applications for detecting viruses, pathogens, bacteria and other biomarkers in liquid samples.

Climate change and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are forming an alarming alliance: Global warming creates new breeding grounds for resistant bacteria. A serious and very real threat to public health – but not quite the doomsday scenario some might make it out to be, says Prof Sabiha Essack from the University of KwaZulu-Natal in Durban, South Africa.

An international research team has now found an approach to lower the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and reduce the associated development of liver fibrosis.

Finding the right antibiotic dose is akin to a Goldilocks problem: give too little, and the infection will persist; too much, and side-effects will override the benefits of the therapy. To get it “just right”, Prof Dr Birgit Koch talks about dosing optimisation in the clinical setting.
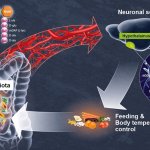
Hypothalamic neurons in an animal model directly detect variations in bacterial activity and adapt appetite and body temperature accordingly.

When treating acute infections, health care providers must quickly identify the best antibiotics for fighting the infection. An automated system provides swift, accurate results for determining the best antibiotics at the right dose.

The COVID-19 testing device can detect coronavirus infection in as little as 30 seconds as sensitively and accurately as a PCR test.

Point-of-care testing (POCT) is a “win-win” scenario for patients and healthcare professionals in delivering care when and where it is needed, according to pathologist Adil Khan, MSc, PhD.
SARS-CoV-2 has heavily impacted global society with high pressure on public health and economics. MolGen is proud to assist in relieving some of the pressure and support the testing framework.
In the human intestine, Escherichia coli is mostly harmless, but in certain conditions causes bladder infections and even sepsis - but why? Researchers went to the bottom of this transformation.

Sepsis is the cause of one in five deaths worldwide, killing nearly 11 million people each year, many of them children. It is also a major cause of disability, affecting millions more. To combat the condition, many hospitals have implemented sepsis performance improvement programmes. A meta-analysis of 50 observational studies showed that these programmes are associated with better compliance…
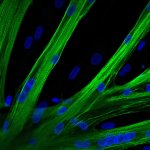
An ECRC research team has introduced CRISPR-Cas9 into human muscle stem cells for the first time using mRNA, thus discovering a method suitable for therapeutic applications.
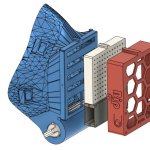
The new 3D-printable mask design promises easy breathing for users while maintaining similar levels of protection against pathogens found in N95 and surgical masks.

An international team of scientists have shown that small and large bacterial populations follow qualitatively different evolutionary paths to develop antibiotic resistance.
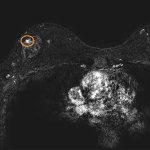
Annual MRI screenings starting at ages 30-35 may reduce breast-cancer mortality by more than 50% among women who carry certain genetic changes in three genes, according to a new modeling analysis.
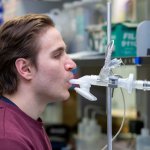
Scientists have confirmed that an inhaled form of COVID vaccine can provide broad, long-lasting protection against the original strain of SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern.

Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen (DZNE) present new findings on the immune response against SARS-CoV-2.

Autokit CH50 Assay is an in vitro diagnostic (IVD) test for the quantitative determination of total complement activity in human serum. The complement system is a part of the immune system that enhances/complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism.

Researchers have developed a diagnostic for Sars-CoV-2 that is capable of differentiating between Covid-19 and the garden-variety bug with fast turnaround.

For many years, antibiotic consumption in France was at an alarming level, resulting in a worryingly constant increase in antibiotic resistance However, a newly-enforced strict national plan appears to be having effect.

The team at the Institute of Medical Device Technology at the University of Stuttgart, Germany, is developing methods to produce top-quality medical devices at affordable prices. Professor Dr Peter Pott, the director of the institute, turns to 3D printers to successfully realize his vision of “high end at low cost”.

An invisible protective wall of UV-C light developed by researchers in Munich could reliably curb the spread of viruses and other pathogens in rooms while allowing total freedom of movement.

A worldwide consortium aims to equip researchers in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) with cheap and accessible methods for sequencing large collections of bacterial pathogens.
To counteract the spread of resistant germs, researchers have developed new drug candidates that are able to render one of the most important hospital germs harmless.
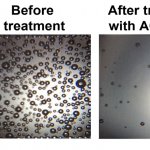
In experiments using saliva samples from COVID-19 patients, the gum, which contains the ACE2 protein, neutralized the virus.

AI-designed Xenobots reveal an entirely new form of biological self-replication—promising for regenerative medicine.

Experts predict that without intervention, the problem of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections could be catastrophic by 2050, killing nearly 10 million people each year.

“Twindemic” is a term that has not yet been in the headlines but is likely to become part of our lexicon as the summer progresses.
The Covid-19 crisis that gripped England between September 2020 and June 2021 can be thought of as a series of overlapping epidemics, rather than a single event, say researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) and the German Cancer Research Center.

Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver inflammation that is triggered by an immunological malfunction. In this case, the immune system falsely recognises the patient's own liver cells as "foreign to the body". The symptoms of this rare liver disease are unspecific, and the exact cause is not yet known. If left untreated, AIH can lead to abnormal scarring (fibrosis) of the liver,…
After infection with SARS-CoV-2, where does the immune system store the memory to provide long-term protection against reinfection? Though numerous studies have examined blood to track immune responses to SARS-CoV-2, a new study of Covid survivors shows that the memory of the infection is primarily stored in T and B cells within the lung and the lymph nodes surrounding the lung.
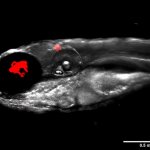
Researchers have found a way to defeat the multi-resistant bacterium Mycobacterium abscessus, a relative of the causes of tuberculosis and leprosy.
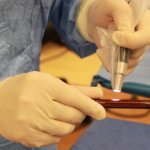
Customizable to individual patients and requiring less than 10 minutes to prepare and use, new surgical implant coating prevented 100% of infections in mice.

Infectious disease diagnostics are notoriously slow. The gold standard for laboratory diagnosis of bacterial and fungal infection involves growing the pathogen from a clinical specimen – an overnight event, or even longer. The healthcare focus is on improving the use of antibiotics for better patient outcomes and reducing the environmental pressures that drive antibiotic resistance. To impact…

A solid diagnosis has always been the first step on any patient’s journey to health. However, diagnostic categories are necessarily oversimplifications. In the last decades, medical professionals and scientists have begun to uncover the true variability in patients’ physiological and biochemical make-up that is the principal cause for individual variations in the way diseases present…

Antibiotic-resistant pathogens have become one of the greatest threats to public health. The basic mechanisms of resistance evolution have been well studied experimentally and are an important research field at Kiel University. An important factor in this context, but one that has received little attention so far, is the population size of the respective pathogen. Over the course of an infection…

Antibiotics have been at the heart of modern healthcare since the 1950s. They are prescribed prior to an operation to minimise the risk of infection after the operation. Or antibiotics are prescribed to fight an infection. This practice, which might seem straightforward at first glance, has proven to cause a number of problems itself: Over the last twenty years, it has become increasingly clear…

Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers in the world, and one of the most difficult to treat. In 2020, an estimated 495,000 individuals worldwide were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer and an estimated 466,000 died, according to statistics from the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer. Most patients with advanced disease die within a year of…
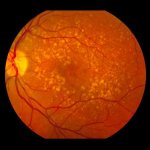
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of blindness in developed countries affecting seven million in total in Germany, from which 500,000 people are suffering from late stage disease, around half of whom are registered as visually impaired. There are two forms of AMD, ‘wet’ and ‘dry’. There are currently no treatments available for the dry form of the disease…
An international research team from Saudi Arabia, Germany, and Jordan has developed a novel pathogen aptasensor swab designed to qualitatively detect, within five minutes, any methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) contamination that remains in a hospital isolation room or other surface following standard decontamination and cleaning.

Researchers at RMIT University in Australia have developed smart wound dressings with built-in nanosensors that glow to alert patients when a wound is not healing properly. The multifunctional, antimicrobial dressings feature fluorescent sensors that glow brightly under UV light if infection starts to set in and can be used to monitor healing progress.
When viruses infect cells, changes in the cell nucleus occur, and these can be observed through fluorescence microscopy. Using fluoresence images from live cells, researchers at the University of Zurich have trained an artificial neural network to reliably recognize cells that are infected by adenoviruses or herpes viruses. The procedure also identifies severe acute infections at an early stage.
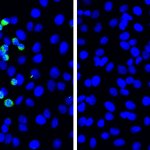
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation resulting from the inflammatory response to coronavirus infection may be the cause of previously unexplained long Covid symptoms—such as fatigue, brain fog, and rashes—that occur in approximately 30% of patients after recovery from initial Covid-19 infection. The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long Covid, as well as an analysis of long Covid…

T2 Biosystems, Inc. announced the its participation in three virtual conferences this summer. The company, which specialises in the rapid detection of sepsis-causing pathogens, will take part in the American Society for Microbiology’s (ASM) and Federation of European Microbiological Societies’ (FEMS) World Microbe Forum; Sepsis Alliance’s inaugural Sepsis Tech and Innovation 2021…
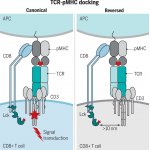
Monash University researchers have provided a fundamental advance regarding how T cells become activated when encountering pathogens such as viruses.

Understanding every step in the life cycle of a virus is crucial for identifying potential targets for treatment. Now, scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria were able to show how a virus from the retrovirus family – the same family as HIV – protects its genetic information and becomes infectious. Furthermore, they show an unexpected flexibility of the virus. This…
Scientists from Hokkaido University have discovered a novel defensive response to SARS-CoV-2 that involves the viral pattern recognition receptor RIG-I. Upregulating expression of this protein could strengthen the immune response in COPD patients.

Antibiotic resistant bacteria are a looming super threat – heralding a time when our drugs will no longer be effective against prevalent infections. Hospitals are already coping with treatment-resistant bacterial infections. Cognizant of the threat and thinking outside the box, BGU scientists and German and American colleagues have developed a pair of 'molecular tweezers' to destroy the biofilm…

The use of Silver-based medical products has always been prevalent in hospital settings to kill bacteria instantly. As the Covid-19 pandemic rages on and many look for practical PPE equipment, manufacturer Suprcare launches its 'Suprmask' with Pure Silver technology. In addition, it can be reused without having to be washed.
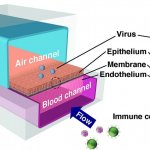
A collaboration spanning four research labs and hundreds of miles has used the organ-on-a-chip (Organ Chip) technology from the Wyss institute at Harvard Univesity to identify the antimalarial drug amodiaquine as a potent inhibitor of infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19. The Organ Chip-based drug testing ecosystem established by the collaboration greatly streamlines the…
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have created an artificial intelligence platform that can identify the specific proteins that allow bacteria to infect the intestines.
Research has identified critical factors that enable dangerous bacteria to spread disease by surviving on surfaces in hospitals and kitchens. The study into the mechanisms which enable the opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa to survive on surfaces, could lead to new ways of targeting harmful bacteria. To survive outside their host, pathogenic bacteria must withstand various…

What happens when patients can no longer breathe on their own and need to be supported by machines? How far does infected air spread throughout a room? And what safety precautions do medical and nursing staff need to take? Respiratory specialists Dr. Dominic Dellweg and Dr. Jens Kerl together with Dr.-Ing. Conrad Völker, Amayu Wakoya Gena, and Dr. Hayder Alsaad from the Department of Building…
Coronavirus researchers under Prof. Rolf Hilgenfeld of the University of Lübeck and Dr. Albrecht von Brunn of the Ludwig-Maximilians University of Munich discovered how SARS viruses enhance the production of viral proteins in infected cells, so that many new copies of the virus can be generated. Other coronaviruses apart from SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 do not use this mechanism, thereby providing a…

The world is still failing to develop desperately needed antibacterial treatments, despite growing awareness of the urgent threat of antibiotic resistance, according to a new report by the World Health Organization. WHO reveals that none of the 43 antibiotics that are currently in clinical development sufficiently address the problem of drug resistance in the world’s most dangerous bacteria.…

An increasing number of bacterial pathogens are resistant to antibiotics. And the most dangerous pathogens share a common feature: a double membrane that is difficult to penetrate. Even when antibiotic agents are able to break into this shell, the bacteria just pump them right out again. But a recently discovered compound called Darobactin manages to circumvent these protective measures and kill…

Does overcoming a SARS-CoV-2 infection protect against reinfection? The “Rhineland Study”, a population-based study conducted by DZNE in the Bonn area, is now providing new findings in this regard. Blood samples taken last year indicate that an important component of immunity – the levels of specific neutralizing antibodies against the coronavirus - had dropped in most of the study…
A consortium of researchers from Russia, Belarus, Japan, Germany and France led by the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology have uncovered the way in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in iron-deficient conditions by utilizing rubredoxin B, a protein from a rubredoxin family that play an important role in adaptation to changing environmental conditions.

Clinicians using a new viral screening test can not only diagnose Covid-19 in a matter of minutes with a portable, pocket-sized machine, but can also simultaneously test for other viruses—like influenza—that might be mistaken for the coronavirus. At the same time, they can sequence the virus, providing valuable information on the spread of Covid-19 mutations and variants. The new test, dubbed…

Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Francis Crick Institute have developed a mass spectrometry-based technique capable of measuring samples containing thousands of proteins within just a few minutes. It is faster and cheaper than a conventional blood count. To demonstrate the technique’s potential, the researchers used blood plasma collected from Covid-19 patients.…

Researchers from Cleveland Clinic’s Florida Research and Innovation Center (FRIC) have identified a potential new target for anti-COVID-19 therapies.
Researchers have developed an innovative method to disrupt the formation of biofilms and thus facilitate the treatment of infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Do BMMFs, the novel infectious agents found in dairy products and bovine sera, play a role in the development of colorectal cancer? Scientists led by Harald zur Hausen detected the pathogens in colorectal cancer patients in close proximity to tumors. The researchers show that the BMMFs trigger local chronic inflammation, which can cause mutations via activated oxygen molecules and thus promote…

In order to monitor and contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2 it is necessary to test large numbers of people on a regular basis in decentralized settings. Researchers of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the Hospital St. Georg in Leipzig, Germany, have developed improved protocols for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The method can detect a positive sample in a pool with 25…

A global group of researchers is calling for better integration of viral genetics, bioinformatics, and public health to enable better pandemic response now and better pandemic preparedness in the future. In a comment piece in the journal Nature, an international collaboration of specialists in viral and genetic analysis, led by Swiss scientists Dr. Emma Hodcroft at the University of Bern and…
Bacteria have many ways to evade the antibiotics that we use against them. Each year, at least 2.8 million people in the United States develop an antibiotic-resistant infection, and more than 35,000 people die from such infections, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control. Most of the mutations known to confer resistance occur in the genes targeted by a particular antibiotic. Other…

Researchers at ZHAW Zurich University of Applied Sciences are working with the Swiss company Osmotex AG to develop a self-disinfecting mask that inactivates viruses at the push of a button. The prototype of this mask made of electrochemical textiles shows an antiviral effect of over 99 percent. Further applications such as sterilizable seat covers are being examined.
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers studied SARS-CoV-2 infections at individual cellular levels and made four major discoveries about the virus, including one that validates the effectiveness of remdesivir – an FDA-approved antiviral drug – as a form of treatment for severe Covid-19 disease. “Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, the way that each individual responds…
Scientific and public health experts have been raising the alarm for decades, imploring public officials to prepare for the inevitability of a viral pandemic. Infectious epidemics seemingly as benign as "the flu" and as deadly as the Ebola virus provided ample warning, yet government officials seemed caught off guard and ill prepared for dealing with Covid-19.

Global greenhouse gas emissions over the last century have made southern China a hotspot for bat-borne coronaviruses, by driving growth of forest habitat favoured by bats. A new study published in the journal Science of the Total Environment provides the first evidence of a mechanism by which climate change could have played a direct role in the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that caused the…
Researchers from the University of Nottingham have discovered a novel antiviral property of a drug that could have major implications in how future epidemics/pandemics – including Covid-19 – are managed. The study, published in Viruses, shows that thapsigargin is a promising broad‑spectrum antiviral, highly effective against SARS-CoV-2, a common cold coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus…
USC researchers have developed a new method to counter emergent mutations of the coronavirus and hasten vaccine development to stop the pathogen responsible for killing thousands of people and ruining the economy.

Clinical diagnostics company Beckman Coulter announced the launch of the DxH 560 AL, a tabletop analyzer geared to reduce the time and resource constraints faced by small to mid-sized laboratories. With the analyzer’s Auto-Loading functionality, closed tube aspiration and walkaway capabilities, users can continually add up to 50 samples, provide safety against blood-borne pathogens and spend…

Researchers at the University of Arizona are developing a Covid-19 testing method that uses a smartphone microscope to analyze saliva samples and deliver results in about 10 minutes. The research team, led by biomedical engineering professor Jeong-Yeol Yoon, aims to combine the speed of existing nasal swab antigen tests with the high accuracy of nasal swab PCR, or polymerase chain reaction,…
Researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) and the University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) at Galveston have discovered what may be the Achilles' heel of the coronavirus, a finding that may help close the door on COVID-19 and possibly head off future pandemics.
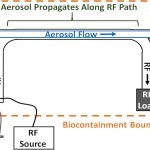
As the pandemic has continued to spread globally, studies indicate the COVID-19 virus may be contained in aerosols that can be generated and spread through breathing, coughing, sneezing, or talking by infected individuals. Researchers are increasingly focused on developing tools and methods to assist in decontaminating surfaces and spaces.

New high-resolution structures of the bacterial ribosome determined by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago show that a single water molecule may be the cause — and possible solution — of antibiotic resistance. The findings of the new study are published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology. Pathogenic germs become resistant to antibiotics when they develop the ability to…
With Covid-19 dominating medical science and human concern, chemists at the University of Sydney have developed a method to quickly and safely synthesise protein vaccines for respiratory diseases for pre-clinical tests. Their approach can be used to test vaccine strategies against novel pandemic pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19.
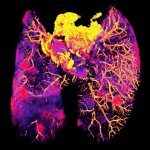
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and the University of Western Australia have developed a new imaging method to see where antibiotics have reached bacteria within tissues. The method could be used to help develop more effective antibiotic treatments, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.

Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) scientists developed the world’s first mobile genome sequence analyzer, a new iPhone app called iGenomics. By pairing an iPhone with a handheld DNA sequencer, users can create a mobile genetics laboratory, reminiscent of the “tricorder” featured in Star Trek.
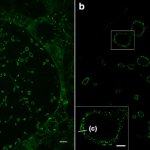
For the first time ever, expansion microscopy allows the imaging of even the finest details of cell membranes. This offers new insights into bacterial and viral infection processes.

Bacterial infections have become one of the biggest health problems worldwide, and a recent study shows that COVID-19 patients have a much greater chance of acquiring secondary bacterial infections, which significantly increases the mortality rate.
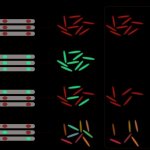
For a slow-growing microbe that multiplies infrequently, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the pathogen that causes tuberculosis (TB) has long puzzled researchers as to how it develops resistance to antibiotics so quickly, in a matter of weeks to months.

Healthcare settings require sharp weapons to fight both hospital-acquired infections and pathogens like SARS-CoV-2. Besides protective equipment, regular room disinfection is one of them. So, why not fog the room? Read more in the MEDICA magazine.

Recent research in Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) has identified two enzymes that can detect Covid-19 RNA as simply as a pregnancy test Jesús Pla, an eminent microbiologist at the Complutense University in Madrid, explained in our exclusive interview. CRISPR technology could help alleviate workloads in packed hospitals and expand testing to primary care and…

Measures to reduce the spread of Covid-19 through non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as mask wearing and social distancing are a key tool in combatting the impact of the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. These actions also have greatly reduced incidence of many other diseases, including influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).

Safety and protection for patients and healthcare professionals during routine procedures is imperative for Fujifilm, which it intends to pursue by constantly innovating its offering of accessories and instruments for endoscopy. The company announced the launch of the Mouthpiece “B1” incorporating a sponge rubber, a droplet reduction accessory, and a drape shield specifically created to catch…

University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists have discovered the fastest way to identify potent, neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.

Russian tech company Connectome.ai is bringing its innovative Directiva.ai hand hygiene teaching and monitoring system to two major clinics owned by the European Medical Center group, the leading private healthcare provider in Moscow and the surrounding region.

Injuries due to contaminated puncture devices are still the most frequent cause of accidents in hospitals. This is a significant source of danger for many employees in the healthcare industry. At this moment in time, there are already more than 20 bloodborne pathogens that we know of. The most dangerous are HBV, HCV and HIV. Recent studies show that it is up to ten times more likely for more…
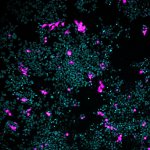
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 is known to infect cells via the receptor ACE2. An international research team under German-Finnish coordination has now identified neuropilin-1 as a factor that can facilitate SARS-CoV-2 entry into the cells’ interior. Neuropilin-1 is localized in the respiratory and olfactory epithelia, which could be a strategically important localization to contribute to…

Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics has emerged as a powerful tool to help study chemical ecology. Recent advances in the technique make it possible to study microbial interactions from complex communities. Laia Castaño-Espriu outlined the role and benefits of MS in this context in her presentation ‘Analysis of microbial ecology by mass spectrometry-based metabolomics techniques’, at the…

In 2019, the Central Laboratory of the Institute for Clinical Chemistry and Pathobiochemistry at the Klinikum rechts der Isar of the Technical University Munich, headed by Professor Peter B Luppa, organised the 4th of the internationally renowned Munich Point-of-Care Testing Symposiums. Dr Andreas Bietenbeck is senior physician at the Institute which for many years has been focusing on…
The fight against bacterial infections, especially those caused by resistant pathogens, is in full swing with the search for new antibiotic agents. The aim is to identify substances that attack the pathogens in a truly novel way. The team at the Center for Systems-Based Antibiotic Research (Cesar) at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) has described in two publications how assess if a new antibiotic…
The present Coronavirus pandemic with all its effects on society – both health and economic – highlights the urgency of developing new therapies for COVID-19 treatment. At the same time, it demonstrates the necessity to become well prepared for new virus infections we may be facing in the future. To help control the current pandemic and brace for novel pathogens that may cause future…
As President Trump claims that he is immune to COVID-19 and isolated reports emerge of reinfection, what is the truth about immunity to COVID-19? To date, there have been six published cases of COVID-19 reinfection, with various other unverified accounts from around the world. Although this is a comparably small fraction of the millions of people known to have been infected, should we be…

The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has decided to award the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020 to Emmanuelle Charpentier from the Max Planck Unit for the Science of Pathogens, Berlin, Germany, and Jennifer A. Doudna from the University of California, Berkeley, USA, “for the development of a method for genome editing”, more commonly known as the 'gene scissors' CRISPR/Cas9.

Researchers at the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin have identified highly effective antibodies against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and are now pursuing the development of a passive vaccination. In this process, they have also discovered that some SARS-CoV-2 antibodies bind to tissue samples from various organs, which could potentially…

Surface disinfection has proved an effective method to control Covid-19 infection, as virologists from the Ruhr University Bochum (RUB) have shown. However, an effective disinfection strategy against Coronavirus must consider various factors, says Professor Eike Steinmann, head of the Department of Molecular and Medical Virology at the RUB.

Researchers have shown why hospital germs adhere strongly to surfaces from which water simply rolls off, but bind so poorly to surfaces that are easily wetted by water.
Researchers at the University of Sheffield have developed a new compound that is able to kill both gram-positive and gram-negative antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
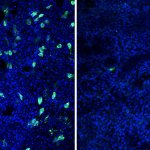
Rhinovirus, the most frequent cause of common colds, can prevent the flu virus from infecting airways by jumpstarting the body's antiviral defenses.
An infection with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 can affect multiple organs. With this in mind, researchers of the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and Cornell University in the US have investigated cellular factors that could be significant for an infection. To this end, they analysed the activity of 28 specific genes in a wide range of human tissues.

The airborne transmission of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 via aerosol particles in indoor environment seems to be strongly influenced by relative humidity. This is the conclusion drawn by researchers from the Leibniz Institute for Tropospheric Research (TROPOS) in Leipzig and the CSIR National Physical Laboratory in New Delhi from the analysis of 10 most relevant international studies on the…

As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to claim lives around the world, much research has focused on the immune system’s role in patients who become seriously ill. A popular theory has it that the immune system gets so revved up fighting the virus that, after several days, it produces a so-called cytokine storm that results in potentially fatal organ damage, particularly to the lungs.

Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a synthetic peptide that can make multidrug-resistant bacteria sensitive to antibiotics again when used together with traditional antibiotics, offering hope for the prospect of a combination treatment strategy to tackle certain antibiotic-tolerant infections.

Antibiotic resistance is an increasing battle for scientists to overcome, as more antimicrobials are urgently needed to treat biofilm-associated infections. However, scientists from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick say research into natural antimicrobials could provide candidates to fill the antibiotic discovery gap.

Chemical binding company Affix Labs has created the first long-lasting surface treatment proven to kill COVID-19. Si-Quat combines a safe and well-established disinfectant and a proprietary chemical binding technique, so that the active ingredient can kill viruses, including SARS-CoV-2. Testing at Portugal’s Biochemistry Institute at the University of Lisbon proves that Si-Quat effectively…

EKF Diagnostics, the global in vitro diagnostics company, announces that it has added a novel viral transport media for the safe sample handling and testing of multiple infectious diseases from a single swab to its product range.

Nanoelectronics and digital technologies R&D and innovation hub Imec recently received NASA funding to test a new technology in a gravity-free environment. Eventually, this will enable astronauts to perform blood tests to monitor their health. We discussed the project and technology with Nicolas Vergauwe, CEO of miDiagnostics, the Leuven firm that developed the diagnostic device, and Susana B…
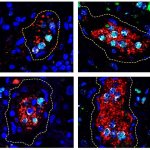
An overactive defense response may lead to increased blood clotting, disease severity, and death from COVID-19. A phenomenon called NETosi is part of an immune response that becomes increasingly hyperactive in people on ventilators and people who die from the disease.
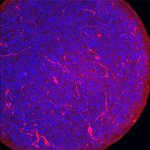
Scientists have found that organoids (tiny tissue cultures made from human cells that simulate whole organs) known as “mini-brains” can be infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
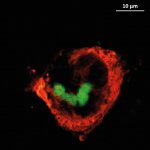
New coatings on implants could help make them more compatible. Researchers at the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have developed a new method of applying anti-inflammatory substances to implants in order to inhibit undesirable inflammatory reactions in the body. Their study was recently published in the "International Journal of Molecular Sciences".
Beckman Coulter announced that its Access SARS-CoV-2 IgG assay has received Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). Beckman Coulter has already shipped tests to more than 400 hospitals, clinics and diagnostics laboratories in the U.S., and has begun distribution of the new antibody test globally to countries that accept the FDA EUA and CE Mark. The…
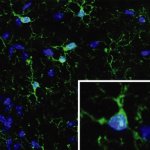
Infections can trigger a particularly strong immune reaction of the body (termed sepsis). In such a sepsis the immune system reacts so strongly that not only the pathogens but also tissues and organs are damaged. In a study with mice, researchers from the Technische Universität Braunschweig were able to show that sepsis can have long-term effects on the brain and learning behaviour even after…
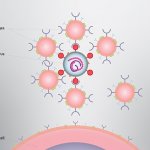
Nanoparticles cloaked in human lung cell membranes and human immune cell membranes can attract and neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture, causing the virus to lose its ability to hijack host cells and reproduce.
A tuberculosis vaccine developed 100 years ago also makes vaccinated persons less susceptible to other infections. While this effect has been recognized for a long time, it is not known what causes it. Together with colleagues from Australia and Denmark, researchers from Radboud university medical center the universities of Nijmegen and Bonn have now presented a possible answer to this question.

In the hustle and bustle of a hospital, properly disinfecting all surfaces in a patient room can be a challenging and time-consuming task. Now, in times of the coronavirus pandemic, it can also be life-threatening. To minimize the risk for their staff, hospitals are utilizing disinfection robots to sanitize surfaces and rooms.

Light microscope for viewing microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi are commonly found in scientific laboratories. A research team from Furtwangen University, the University of Tübingen and Carl Zeiss Vision International GmbH, Aalen, examined more closely their role as potential vectors of infectious pathogens. „Very little was known about this until now," explains the head of the…

Siemens Healthineers announced today that it is now shipping worldwide its laboratory-based total antibody test1 to detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibodies in blood.

Researchers at Hokkaido University have succeeded in detecting anti-avian influenza virus antibody in blood serum within 20 minutes, using a portable analyzer they have developed to conduct rapid on-site bio tests. If a suitable reagent is developed, this technology could be used to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, the causative virus of COVID-19.

A team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) in Stuttgart invented a tiny microrobot that resembles a white blood cell travelling through the circulatory system. It has the shape, the size and the moving capabilities of leukocytes and could perhaps be well on its way – in a rolling motion of course – to revolutionize the minimally invasive treatment of…
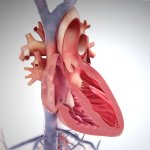
COVID-19 can cause serious cardiovascular complications including heart failure, heart attacks and blood clots that can lead to strokes, emergency medicine doctors at the University of Virgina report in a new scientific paper. They also caution that COVID-19 treatments can interact with medicines used to manage patients’ existing cardiovascular conditions.
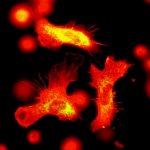
Blood stem cells have a surprising ability. In addition to ensuring the continuous renewal of blood cells, they keep track of past infections so that faster and more effective immune responses can be triggered in the future.
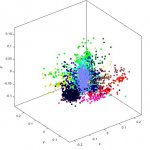
Using machine learning, a team of Western computer scientists and biologists have identified an underlying genomic signature for 29 different COVID-19 DNA sequences. This new data discovery tool will allow researchers to quickly and easily classify a deadly virus like COVID-19 in just minutes – a process and pace of high importance for strategic planning and mobilizing medical needs during a…

Scientists at the University of Alberta have shown that the drug remdesivir is highly effective in stopping the replication mechanism of the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, according to new research published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

European photonics scientists are developing an ultrasensitive laser sensor that detects coronavirus at the earliest point of infection from a saliva or nasal swab in minutes.

In diagnostics, it sometimes makes sense to follow your nose. During the Labmed Forum at Medica, Dr Beniam Ghebremedhin and Dr Simona Cristescu discussed the diagnostic potential of breathomics – the analysis of a patient’s exhaled air for disease indicators.

How long can coronavirus persist on surfaces such as door handles or hospital nightstands? How can the virus be destroyed effectively? A research team from Greifswald and Bochum, Germany, collected the answers scientists can currently offer to these and other pertinent questions and published them in the Journal of Hospital Infection.