Image source: Bokelmann et al., Nature Communications 2021 (CC-BY 4.0)
News • Improved Coronavirus detection
Low-cost and fast Covid-19 test uses pool of gargle lavage samples
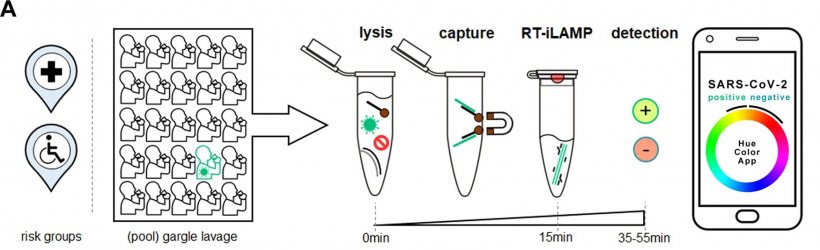
In order to monitor and contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2 it is necessary to test large numbers of people on a regular basis in decentralized settings. Researchers of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the Hospital St. Georg in Leipzig, Germany, have developed improved protocols for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. The method can detect a positive sample in a pool with 25 uninfected samples in less than one hour.
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) is the most widely used diagnostic method to detect RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. However, it requires expensive laboratory equipment and global shortages of reagents for RNA purification has increased the need to find simple but reliable alternatives. One alternative to the qPCR technology is RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification). This test amplifies the desired target sequences of the virus at a constant temperature, using minimal equipment compared to qPCR. In 2020, it was adapted to the detection of SARS-CoV-2. It was also shown that instead of a swab, which many people find unpleasant, it can be performed on gargle lavage samples.
The researchers published their findings in Nature Communications.
Image source: Bokelmann et al., Nature Communications 2021 (CC-BY 4.0)
First author Lukas Bokelmann and colleagues have now developed an improved colorimetric RT-LAMP assay, called Cap-iLAMP (capture and improved loop-mediated isothermal amplification), which extracts and concentrates viral RNA from a pool of gargle lavage samples. After a short incubation, the test result – orange/red for negative, bright yellow for positive – can be interpreted visually or by using a freely available smartphone app.
The improved testing method outperforms previous similar methods. “Cap-iLAMP drastically reduces false positives and single infected samples can be detected in a pool among 25 uninfected samples, thus reducing the technical cost per test to only about 1 Euro per individual”, says senior author Stephan Riesenberg, a researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. “Our method overcomes problems associated with standard RT-LAMP and could also be applied to numerous other pathogens.”
Source: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
08.03.2021





