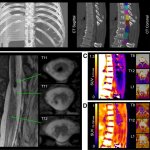
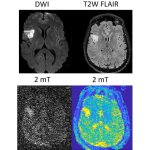
News • Remote sampling
Home blood test for Alzheimer's shows promise
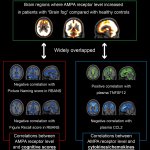
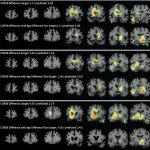
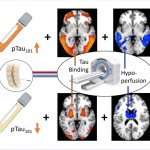
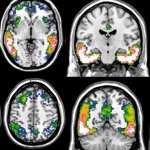
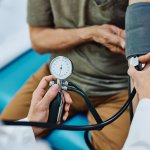
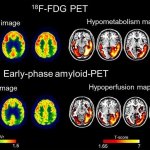
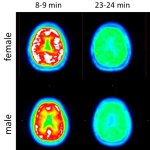
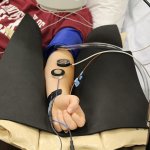
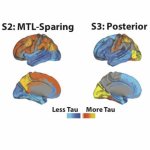
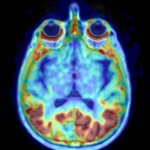
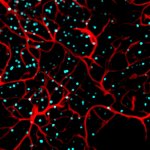
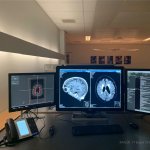
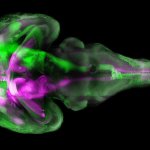
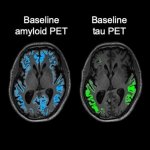
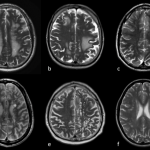
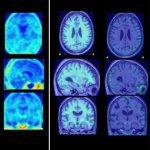
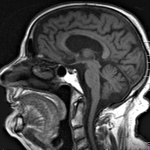
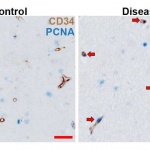
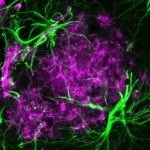
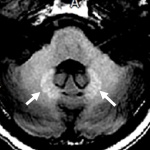
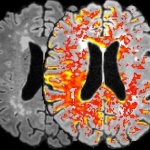
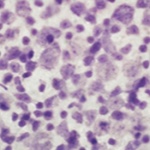
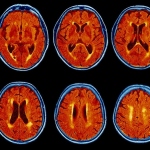
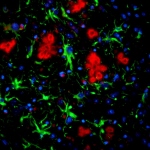
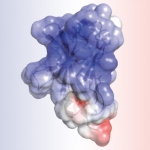
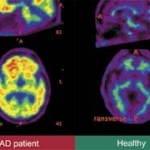
An international study shows that Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers can be accurately detected using simple finger-prick blood samples that can be collected at home and mailed to a laboratory.