PET scans to diagnose Alzheimer's disease
The so-called 11-labeled Pittsburgh Compound B ([11C]PiB) type of positron emission tomography (PET) may be useful in a non-invasive assessment of the formation of Alzheimer's disease-related plaques, according to a study that will appear in the October 2008 issue of Archives of Neurology.
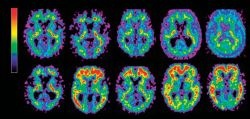
Plaques in the brain made of beta-amyloid and other compounds are considered hallmarks of the development of Alzheimer's disease, according to background information in the article. Currently, the only reliable way to assess the aggregation of these compounds in the brain is through analyzing brain tissue samples obtained during life or autopsy after death—"a major methodological obstacle considering clinical drug trials of early Alzheimer's disease," the authors note.
Ville Leinonen, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Kuopio, Finland, and colleagues studied 10 patients without severe dementia who had undergone a biopsy of their frontal cortex because they were suspected of having normal-pressure hydrocephalus, an abnormal increase of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Cognitive impairment is a symptom of both Alzheimer's disease and normal-pressure hydrocephalus, and 22 percent to 42 percent of patients with symptoms of normal-pressure hydrocephalus have brain lesions characteristic of Alzheimer's disease.
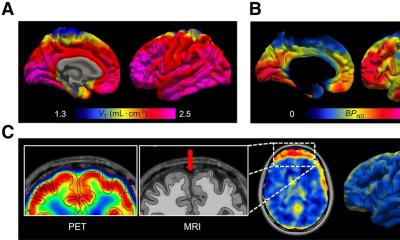
Among the participants, six had beta-amyloid plaques in their tissue samples, while four displayed no Alzheimer's disease–related brain changes. The patients were injected with a marker known as carbon 11–labeled Pittsburgh Compound B ([11C]PiB) and then underwent a 90-minute PET scan.
Results of the scan indicated that patients who had beta-amyloid plaques in their brain biopsy specimen displayed a higher uptake of [11C]PiB in certain brain areas as compared with those who did not have such accumulations.
"This study supports the use of [11C]PiB PET in the evaluation of beta-amyloid deposition in, for example, mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's disease or normal-pressure hydrocephalus," the authors write. "Large and prospective studies are required to verify whether [11C]PiB PET will become a tool in diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. Another potential use of [11C]PiB would be the quantitative monitoring of beta-amyloid deposits in the brain in subjects under treatment in pharmaceutical trials of early Alzheimer's disease targeting amyloid accumulation."
Picture Courtesy: Archives of Neurology; American Medical Association, Ville Leinonen et. al.
12.08.2008