News • AI detects unseen connection
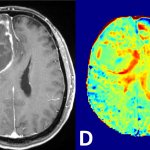
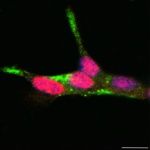
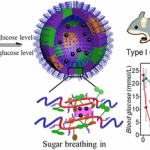
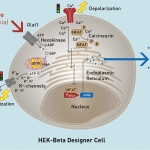
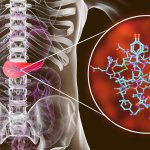
Insulin resistance identified as risk factor for cancer
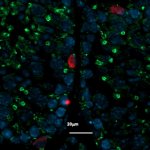
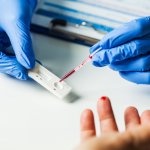
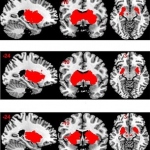
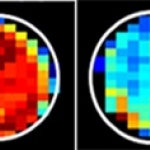
Not just linked to diabetes: For the first time, researchers demonstrated that insulin resistance is a risk factor for 12 types of cancer, including uterine and breast cancer.