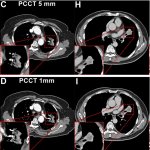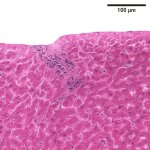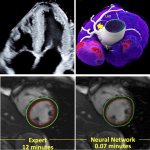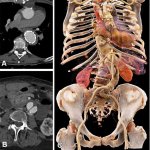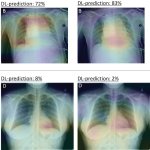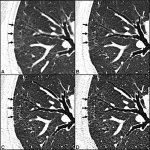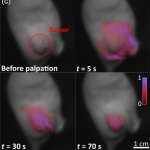
News • Advance in embryo selection
"Invisible" culture dishes improve the odds for IVF
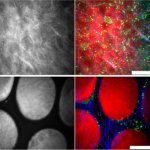
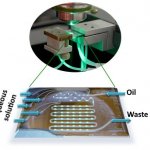
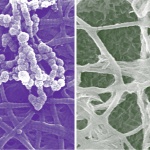
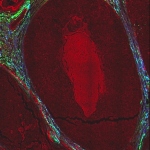
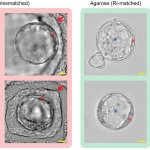
Selecting the healthiest embryo is one of the most important steps in in‑vitro fertilization, yet it remains one of the most uncertain. A new type of hydrogel offers hope for more successful IVF.