News • Public health compliance
Epidemic spread: individual behaviour matters
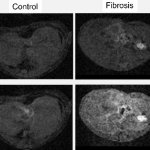
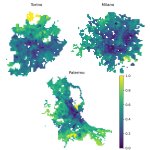
In an epidemic setting, even a small proportion of citizens who do not follow public health measures can amplify the spread of contagions and make them expand faster, a new study reveals.