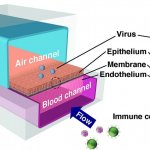
News • Reserach on side effects
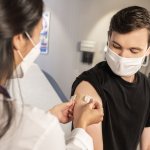
Covid vaccine and decrease in childbirth: study debunks fertility-related rumours
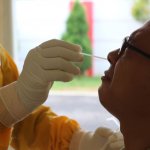
Can a Covid-19 vaccination reduce fertility? A new study from Linköping University finds no evidence to back up rumours naming vaccinations as a cause behind a decrease in childbirth.