News • Data submission on skin symptoms and vaccine
Monkeypox: International registry launched
The World Health Organization and the White House have declared the growing monkeypox outbreak a public health emergency, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommending that people seek medical care immediately if they develop a new, unexplained skin rash or lesion on any part of their body that they think could be monkeypox.
Image source: NIAID, Monkeypox Virus (52132066310), CC BY 2.0
Thanks to a newly launched, comprehensive monkeypox registry, health professionals can share data on the skin symptoms of the disease and the vaccine to improve patient care. “The American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatologic Societies created a monkeypox registry to help health professionals better understand the skin symptoms of the monkeypox virus and skin reactions to vaccines used to prevent it,” said board-certified dermatologist Esther E. Freeman, MD, PhD, FAAD, a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Monkeypox Task Force. “This registry will allow physicians and health care professionals to share valuable information about the cases that they are seeing, which helps us identify dermatologic manifestations of the monkeypox virus.”
Any health care professional taking care of patients with monkeypox or taking care of patients who have received a smallpox/monkeypox vaccine and developed a skin reaction to a vaccine, can contribute to the registry by filling out a brief online form. Patient identifiers such as name or date of birth will not be collected. All de-identified information is kept strictly confidential and will only be shared with researchers compiling information.
Monkeypox is a contagious disease caused by a virus. People who contract monkeypox may have as few as one or two bumps on their skin, and the bumps can look like a blister, pus-filled bump, or open sore. Many may not have a fever or flu-like symptoms. Monkeypox typically lasts two to four weeks. “During this particular outbreak, we’re seeing that the rash may start in the groin, genital region, around the anus, or around and in the mouth or throat — and sometimes stay in the spot that it started instead of spreading," said Freeman. "While the monkeypox rash can be mistaken for chickenpox, shingles, or herpes, there are differences between these rashes. A board-certified dermatologist can narrow down which disease is causing the rash by looking at the pattern of the rash and where the rash appears.” If the dermatologist suspects monkeypox is the cause, they will swab the skin lesion and send it to a lab, where a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test will be performed.
People who have been vaccinated against smallpox may be less likely to develop monkeypox. The vaccine is 85% effective in preventing monkeypox, yet many people have not received it because the last routine smallpox vaccines were given in the United States in 1972 due to the elimination of smallpox.
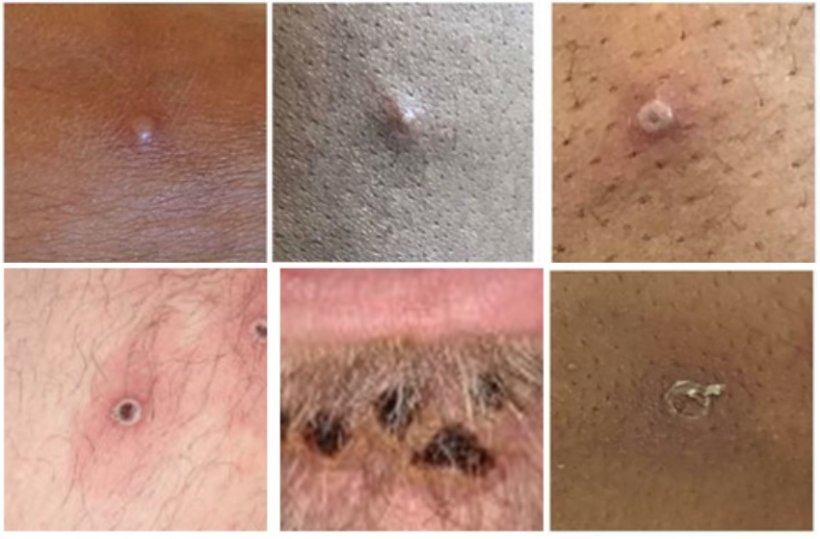
Image source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Treatment options for monkeypox are limited. Some antiviral medications are being used to treat people who test positive for monkeypox and are at risk of getting severely ill. “The monkeypox registry is an important resource to help health professionals improve identification of the disease and help prevent it from spreading further,” said board-certified dermatologist George J. Hruza MD, MBA, FAAD, chair of the American Academy of Dermatology’s Monkeypox Task Force. “The better informed we are, the more equipped we will be to correctly diagnose and treat this infectious disease and identify any potential skin reactions patients experience from the vaccine.”
The American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatologic Societies created a similar registry on the skin signs of Covid-19, as well as skin reactions to the Covid-19 vaccine, in April 2020. “The data from the registry has led to the identification of a variety of different skin reactions that are associated with Covid-19,” said Dr. Freeman. “Some reactions are milder, like Covid toes, and others are more severe. People have a large variability in their immune response to the Covid-19 virus and the vaccines, which causes the skin to react differently for each person. We are hoping to gain a similar understanding of monkeypox through this registry.”
Dermatologists are the experts in the diagnosis and treatment of skin rashes. If you have a rash or bump on your skin that you suspect may be monkeypox and you don’t know what caused it, make an appointment to see a board-certified dermatologist.
Source: American Academy of Dermatology
14.09.2022