News • Neurosciences
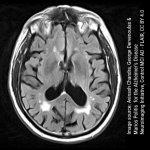
New insights on the onset of Huntington's disease
Why does Huntington’s disease begin at very different ages? Using advanced AI techniques, neuroscientists from the University of Barcelona found a way to better answer this question.