Article • Hospital hygiene
Breaking chains of infection to combat antimicrobial resistance
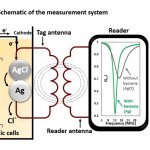
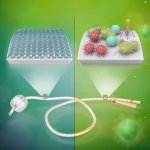
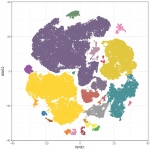
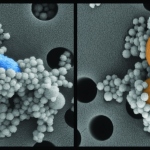
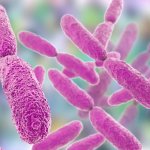
With antimicrobial resistance causing over 5 million deaths annually, rapid outbreak detection is critical. A German lab demonstrates how FTIR spectroscopy can transform hospital infection control.