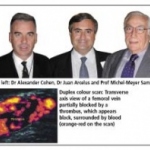
News • Promising trial results from Spain
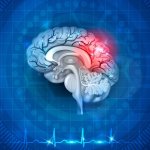
Clot-dissolving drug after thrombectomy may improve stroke recovery
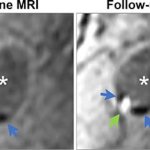
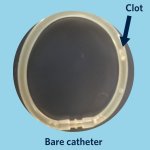
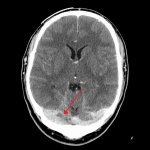
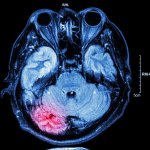
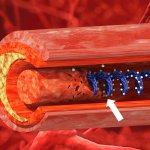
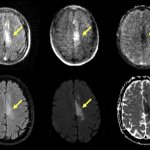
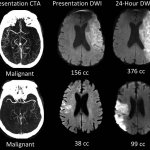
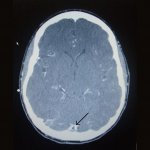
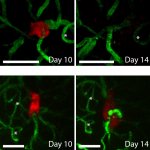
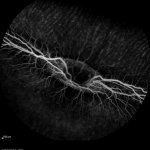
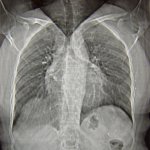
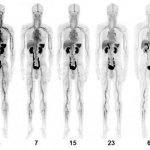
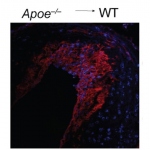
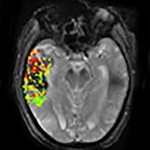
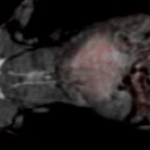
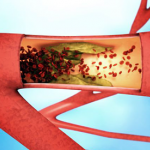
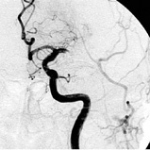
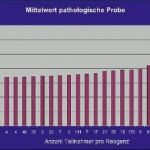
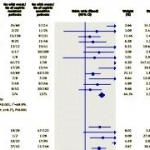
Even after a blood clot is removed from a large brain artery via thrombectomy, administering the thrombolytic drug alteplase to the area may improve stroke recovery, a new trial from Spain shows.