Article • Respiratory health
Pulmonary embolism in pregnancy: diagnostic pathways under scrutiny
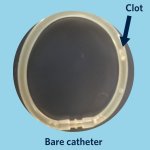
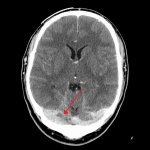
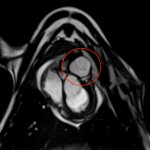
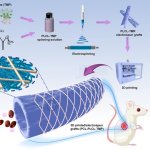
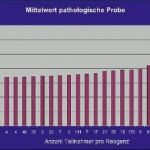
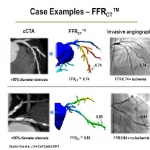
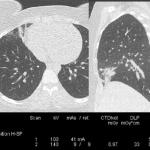
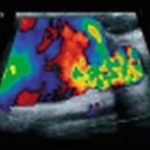
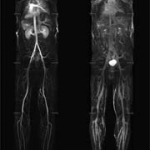
Pulmonary embolism (PE) remains one of the leading causes of maternal mortality. At the French Thoracic Society Spring Days in May, Dr Aurélie Dehaene, radiologist at European Hospital in Marseille, France, reviewed diagnostic strategies for suspected PE during pregnancy, with a focus on clinical algorithms and optimized imaging protocols.