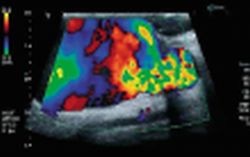
Advanced Dynamic Flow (ADF)
Ultrasound scanning with CCDS is an established technique in shunt diagnostics and allows non-invasive assessment of vascular flow. Stenosing changes to walls of vessels used as a dialysis shunt should be detected as early as possible to avoid occlusion by a thrombus. High occlusion rates with volume flow reduced by up to 45% in one year demand ultrasound screening. The risk of haemodynamically significant stenosis of a fistula is, furthermore, increased by frequent injections and radiological procedures. Complications such as stenosis or thrombosis of the shunt vein or a venous aneurysm can be diagnosed safely and precisely by CCDS. However, the quantitative evaluation of anastomotic stenoses is more difficult. Haemodynamic parameters such as maximum systolic peak velocity provide only limited insights. The same holds true for direct flow assessment as movement artefacts cause significant vascular distortion . The aim of our investigation was to perform flow imaging in cases of pathological shunt changes, for example an anastomotic stenosis, using Advanced Dynamic Flow (ADF) and intra-arterial DSA. We thus compared conventional colour Doppler with Advanced Dynamic Flow in a prospective, systematic study.
This article was first published in the VISIONS, issue 11/2007, a publication of Toshiba Medical Systems
29.08.2007