News • A £15.5 million price tag
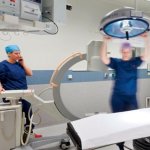
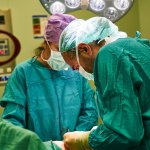
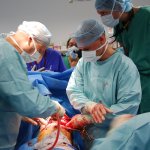
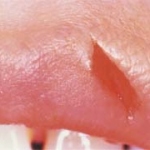
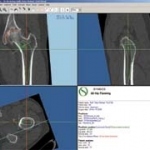
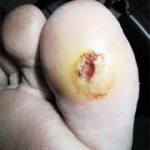
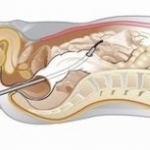
Avoidable knee surgery cancellations: a costly, painful problem
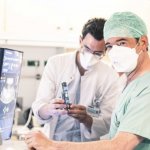
Thousands of NHS knee replacement operations are cancelled at short notice every year, many for avoidable reasons, a new study shows. This costs the NHS millions of pounds and increases waiting times.