News • At least 18 years of reduced risk
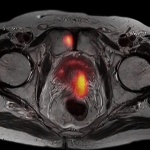
Cervical cancer: study confirms long-term protection from HPV vaccination
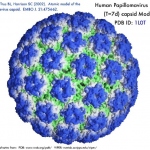
Vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV) reduces the risk of cervical cancer for at least 18 years, according to a new study. There were no signs of waning protection over time.