News • Promising protein analysis tool
New blood test to enable rapid diagnosis of rare genetic diseases
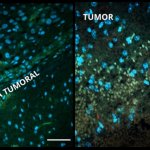
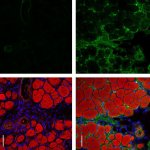
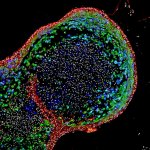
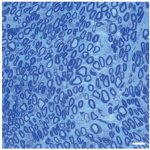
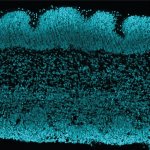
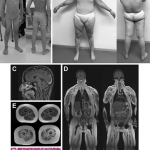
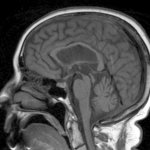
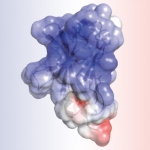
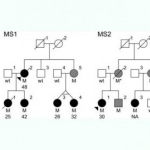
An Australian research team has developed a blood-based method of analysing thousands of proteins in a single, untargeted test. This potentially enables rapid diagnosis of many rare genetic diseases.