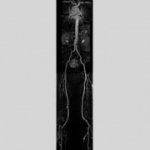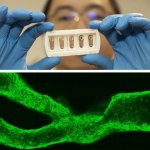
News • 3D printed blood vessels
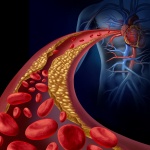
'Artery on a chip' could unravel secrets of strokes
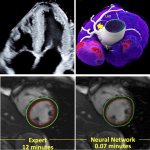
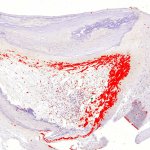
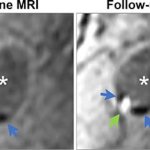
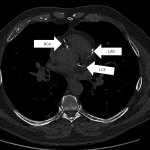
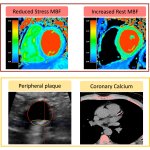
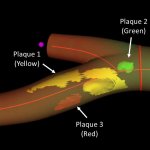
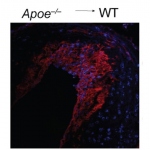
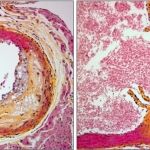
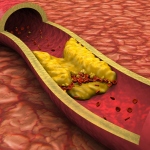
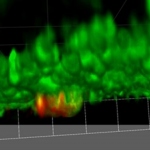
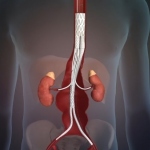
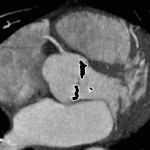
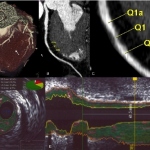
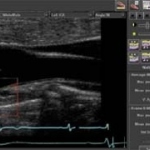
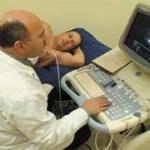
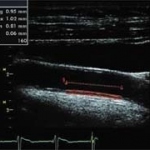
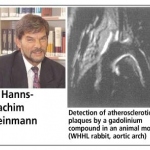
Researchers have developed a new 3D printing technique for blood vessels on glass. This could be a tool for studying stroke causes and testing patient-specific medications without animal testing.