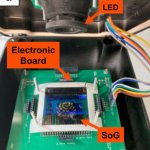
News • Early thoracic malignancy screening
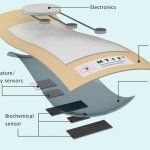
Developing a breath test for lung cancer with biosensors and AI
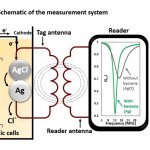
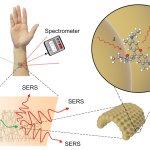
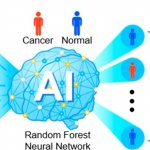
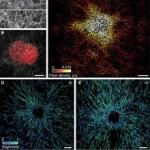
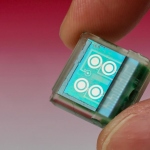
A biosensor that identifies volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath could be used in conjunction with AI to detect various thoracic cancers including lung cancer.