A "palm" for biodetection
Scientists in Singapore are reporting their development of a complete, palm-sized sensor that can detect disease-causing microbes, toxins, and other biological threats instantly without the need for an external power source or a computer.
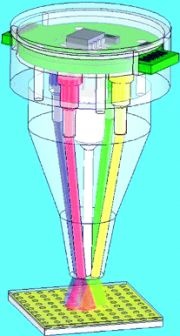
The long-awaited device, ideal for remote medical clinics, battlefields, and other sites, represents the next-generation of faster, simpler biosensors, according to a study scheduled for the August 1 issue of ACS' Analytical Chemistry, a semi-monthly journal.
In the new study, Pavel Neuzil and Julien Reboud from the Institute of Microelectronics at the Singapore Science Park, explain that the new device uses an existing method for detecting DNA, proteins or cells based on their interaction with light shown on the nanostructured surface when these materials come into contact with it.
Most existing biosensors of this type require the use of an external power source, a complex and costly analyzer and rely on an external personal computer to report the results. Their self-contained analyzer relies on simpler components, such as four light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that light up in specific patters to produce test results without a computer, the researchers say.
This article is adapted from the original press release.To read the original publication, click here.
Pictures: Pavel Neuzil, Julien Reboud; Institute of Microelectronics, Singapore
22.07.2008