News • In vitro disease models
'Intrepid' research to advance cancer therapies
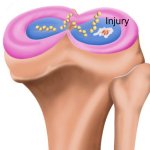
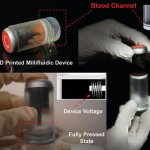
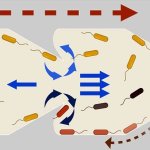
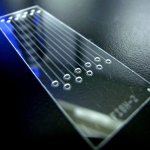
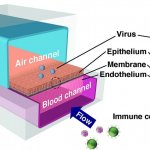
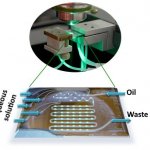
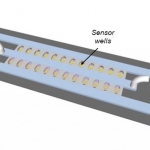
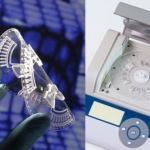
A major new initiative aims to enable the development of advanced, specific and highly reproducible human in vitro models for greater understanding of disease and the acceleration of new medicines.