News • UHR, PCCT, and more
Integrated imaging solutions on display at RSNA 2025
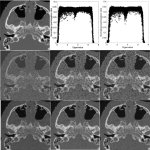
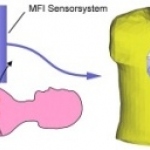
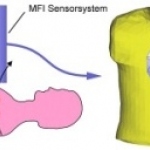
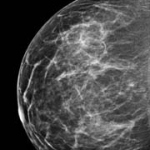
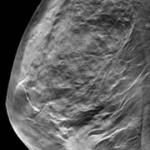
Dunlee will present its portfolio of integrated imaging solutions at RSNA 2025 in Chicago, Illinois. The company will demonstrate technologies for diagnostic and therapeutic imaging applications, including developments in Ultra-High Resolution and Photon Counting CT (UHR & PCCT), components for MRI-guided breast biopsies, and onboard imaging systems for radiation therapy.