Image: Second Bay Studios
News • Subdermal quantum tattoo
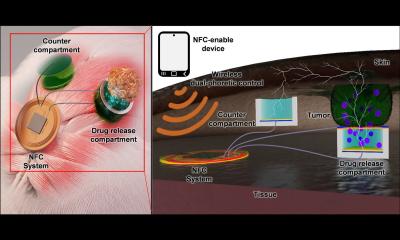
Nano-patch stores medical information under the skin
Every year, a lack of vaccination leads to about 1.5 million preventable deaths, primarily in developing nations. One factor that makes vaccination campaigns in those nations more difficult is that there is little infrastructure for storing medical records, so there’s often no easy way to determine who needs a particular vaccine.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have now developed a novel way to record a patient’s vaccination history: storing the data in a pattern of dye, invisible to the naked eye, that is delivered under the skin at the same time as the vaccine.
The research is now published in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
In order to be protected against most pathogens, one needs multiple vaccinations. In some areas in the developing world, it can be very challenging to do this
Ana Jaklenec
The researchers showed that their new dye, which consists of nanocrystals called quantum dots, can remain for at least five years under the skin, where it emits near-infrared light that can be detected by a specially equipped smartphone. McHugh and former visiting scientist Lihong Jing are the lead authors of the study. Ana Jaklenec, a research scientist at MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, and Robert Langer, the David H. Koch Institute Professor at MIT, are the senior authors of the paper.
Several years ago, the MIT team set out to devise a method for recording vaccination information in a way that doesn’t require a centralized database or other infrastructure. Many vaccines, such as the vaccine for measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR), require multiple doses spaced out at certain intervals; without accurate records, children may not receive all of the necessary doses. “In order to be protected against most pathogens, one needs multiple vaccinations,” Jaklenec says. “In some areas in the developing world, it can be very challenging to do this, as there is a lack of data about who has been vaccinated and whether they need additional shots or not.”
To create an “on-patient,” decentralized medical record, the researchers developed a new type of copper-based quantum dots, which emit light in the near-infrared spectrum. The dots are only about 4 nanometers in diameter, but they are encapsulated in biocompatible microparticles that form spheres about 20 microns in diameter. This encapsulation allows the dye to remain in place, under the skin, after being injected.
Recommended article
Article • Smart patch
ELSAH: A wearable to determine biomarkers
The EU four-year project ELSAH, which began at the dawn of 2019, aims to design a wearable to enable continuous determination of biomarker concentrations. Project coordinator Dr Joerg Schotter, Molecular Diagnostics, Centre for Health & Bioresources, AIT Austrian Institute of Technology GmbH, explains the project’s objectives and potential applications for the planned wearable.
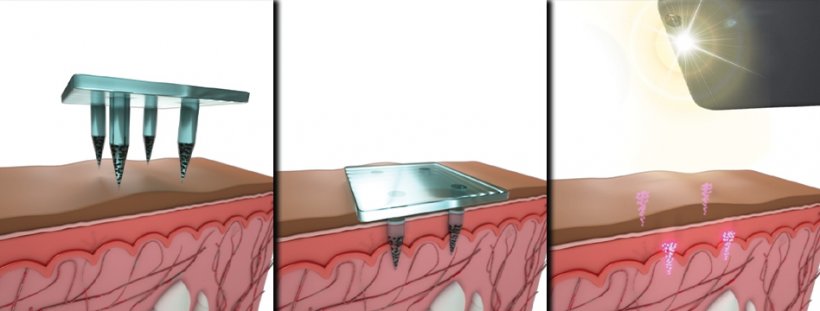
The researchers designed their dye to be delivered by a microneedle patch rather than a traditional syringe and needle. Such patches are now being developed to deliver vaccines for measles, rubella, and other diseases, and the researchers showed that their dye could be easily incorporated into these patches. The microneedles used in this study are made from a mixture of dissolvable sugar and a polymer called PVA, as well as the quantum-dot dye and the vaccine. When the patch is applied to the skin, the microneedles, which are 1.5 millimeters long, partially dissolve, releasing their payload within about two minutes.
By selectively loading microparticles into microneedles, the patches deliver a pattern in the skin that is invisible to the naked eye but can be scanned with a smartphone that has the infrared filter removed. The patch can be customized to imprint different patterns that correspond to the type of vaccine delivered. “It’s possible someday that this ‘invisible’ approach could create new possibilities for data storage, biosensing, and vaccine applications that could improve how medical care is provided, particularly in the developing world,” Langer says.
Tests using human cadaver skin showed that the quantum-dot patterns could be detected by smartphone cameras after up to five years of simulated sun exposure. The researchers also tested this vaccination strategy in rats, using microneedle patches that delivered the quantum dots along with a polio vaccine. They found that those rats generated an immune response similar to the response of rats that received a traditional injected polio vaccine. “This study confirmed that incorporating the vaccine with the dye in the microneedle patches did not affect the efficacy of the vaccine or our ability to detect the dye,” Jaklenec says.
The researchers now plan to survey health care workers in developing nations in Africa to get input on the best way to implement this type of vaccination record keeping. They are also working on expanding the amount of data that can be encoded in a single pattern, allowing them to include information such as the date of vaccine administration and the lot number of the vaccine batch. The researchers believe the quantum dots are safe to use in this way because they are encapsulated in a biocompatible polymer, but they plan to do further safety studies before testing them in patients. “Storage, access, and control of medical records is an important topic with many possible approaches,” says Mark Prausnitz, chair of chemical and biomolecular engineering at Georgia Tech, who was not involved in the research. “This study presents a novel approach where the medical record is stored and controlled by the patient within the patient’s skin in a minimally invasive and elegant way.”
Source: Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
21.12.2019