News • Dynamic supramolecular peptide therapy
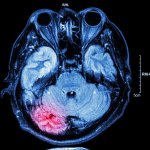
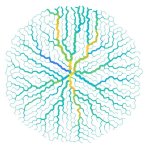
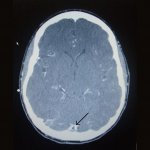
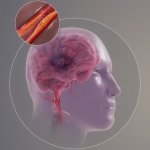
Injection could protect the brain after a stroke
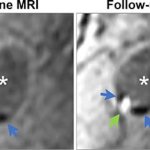
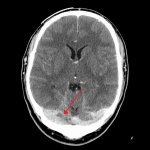
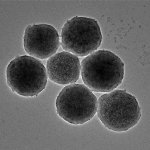
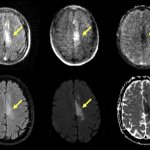
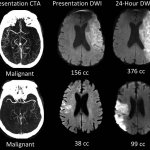
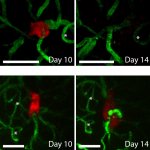
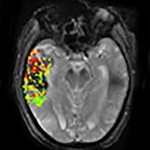
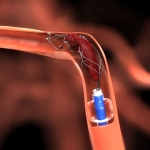
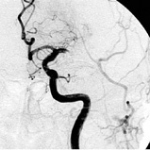
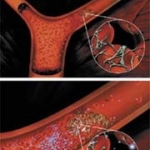
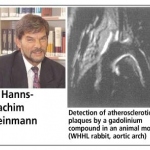
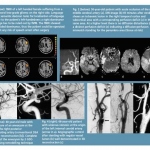
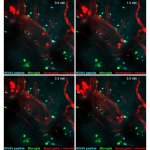
Scientists from Northwestern University have developed an injectable regenerative nanomaterial that helps protect the brain during the vulnerable window after a stroke.