Stroke - Changing radiology assistants’ role speeds diagnoses
Report: Mark Nicholls
A key development at the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH), east of England, has seen a change in the role of radiology assistants: They now help to prepare patients for radiology scans and look after them -- work previously undertaken by radiographers. The change now allows radiographers more time to concentrate on scanning patients, resulting in faster scanning with quicker diagnosis and the commencement of therapy for stroke patients within the crucial three-hour time window.
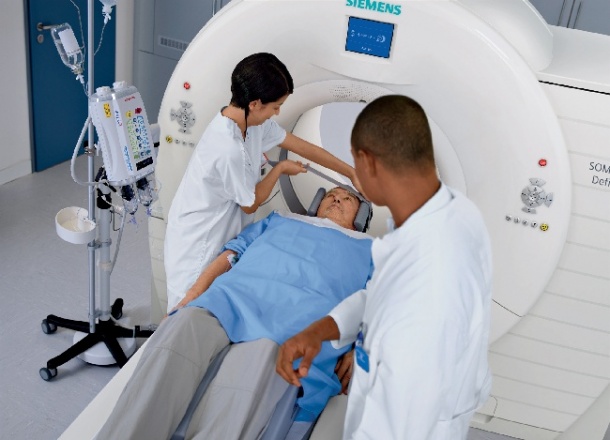
The simple changes to how acute stroke services have been redesigned and improved to achieve faster access to CT brain scans at NNUH have been highlighted by the Department of Health as an example of best practice in brain scanning care for stroke patients in the UK.
The initiative was coordinated by radiographer Chris West, lead NNUH radiographer for CT scanning, and consultant stroke physician Dr Kneale Metcalf, who said that the stroke services were developed and redesigned around hyper-acute care, which has permitted earlier CT scanning and thrombolysis for ischaemic stroke patients. The unit is now obtaining twice as many scans within the first 24 hours, up from 40% to 80%. ‘In patients needing very urgent scans, within the first half an hour of coming through the door, we have put in place processes to do that and we are doing it robustly, 24 hours a day. Interacting with people on the ground within the CT scanning room allows us to arrange urgent scans; consequently, patient care is definitely better.’
The Radiology and Improving Stroke Services video forms part of the NHS Quality, Innovation, Productivity and Prevention (QIPP) programme and is being used to help other NHS hospitals understand more about improving the quality and productivity of such services.
NNUH serves a rural area of the UK, where fast access to CT scans is essential for patients with stroke caused by a blood clot. This allows stroke consultants to diagnose the type of stroke and authorise the administration of thrombolytic drugs within the critical period, significantly improving a patient’s chance of a better recovery, or beginning other treatments.
Chris West pointed out that radiology now has a central role in the treatment of stroke patients. ‘‘It sits centrally to the delivery of those services right from the point the paramedic identifies the patient and calls that case into hospital,’ he said. ‘A stroke assessment nurse is waiting to assess the patient and then refer them straight to us. Previously this would have taken hours to achieve. Now, once the decision to image has been made, we can image them within 10 minutes. As allied health professionals we are in a really good position to influence the way patients are treated because we are right at the centre of a patient’s care pathway.
‘We know what works well, and what doesn't,’ he added. ‘We can identify where the constraints are and then unlock them to deliver a better service.’
NNUH first introduced a stroke thrombolysis service in December 2008; from June 2009 this became a 24/7 service.
The hospital is also currently investing in four new CT scanners - including a Siemens Definition Flash - to provide a cutting-edge diagnostic service for patients.
14.05.2010