News • Research on Antrodia cinnamomea
Promising fungal compound to fight cancer and inflammation
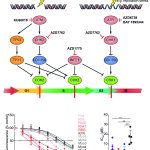
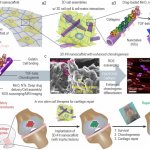
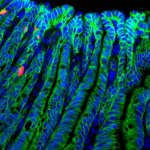
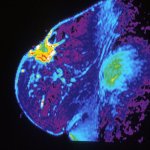
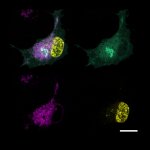
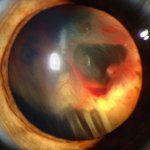
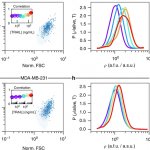
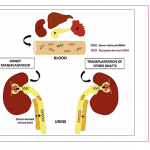
Studies have found that natural polysaccharides from a medical fungus endemic to Taiwan can not only effectively inhibit inflammation, but also fight the proliferation of lung cancer cells.