News • Exploring metastatic potential
AI predicts risk of cancer metastases
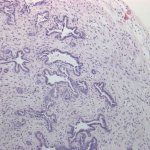
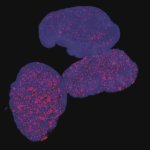
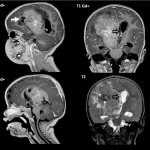
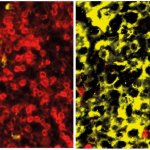
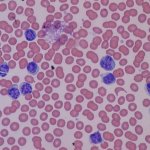
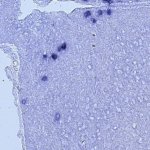
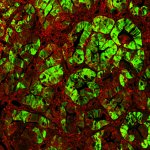
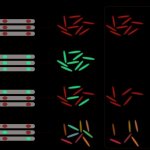
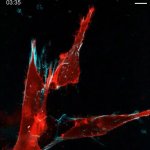
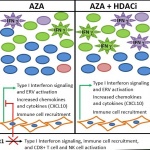
Why do some tumours spread while others remain localised? Using colon cancer cells, scientists pinpointed the criteria that influence metastasis risk, and identified a way to assess its probability.