News • Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
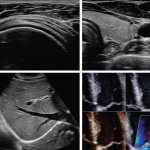
Blood test for ME/CFS unveiled
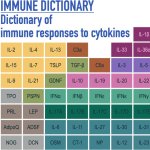
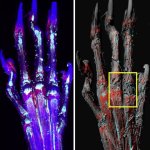
Chronic fatigue (ME/CFS) affects millions worldwide, but is poorly understood and has long lacked reliable diagnostic tools. Now, a new blood test claims to diagnose the condition with 96% accuracy.