
News • Assessing infection risk
Predicting neonatal sepsis with vaginal microbial swabs
A new study shows that analyzing bacteria from vaginal swab samples taken at delivery could help predict the risk of neonatal sepsis.

A new study shows that analyzing bacteria from vaginal swab samples taken at delivery could help predict the risk of neonatal sepsis.
Reseachers show how Candida albicans – a fungus living in our body – can make melanoma more aggressive. The results pave the way for antifungal therapies to complement skin cancer treatments.
Chemotherapy does more than kill cancer cells: It reshapes the gut microbiome, making the body less permissive to metastasis. This finding opens new avenues for adjuvant strategies.

New research shows that a harmless strain of Klebsiella – discovered by chance in laboratory experiments – can eliminate infections and reduce gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).

Scientists developed an AI-based approach to diagnose colorectal cancer from different microbial subgroups in the gut microbiota – a non-invasive and low-cost alternative to colonoscopy screening.
The vaginal microbiome is a largely overlooked area of medicine that could dramatically improve outcomes for common infections, infertility and even cancer for millions of women, a new review finds.

Antibiotics are known for disrupting the microbiome in the gut and thus paving the way for diseases. However, many common non-antibiotics also have this effect, a new study shows.

Microbiota composition can help prevent pathogenic bacteria from proliferating, known as the barrier effect. Now, scientists have identified seven bacteria involved, paving the way for new therapies.

Finding ways to target antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a scientific and medical priority. A consortium of researchers identified a compound capable of blocking a key protein for virulence, thus “disarming” the pathogenic bacteria.

The gastrointestinal microbiome holds valuable information that can help predict whether immunotherapy will be successful against melanoma. A new “gut-on-a-chip” is designed to do exactly that.
Researchers explore the connection between the gut and the brain and its impact on the onset of psychiatric and neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s.

Experts have used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to better understand the impact a gluten free diet has on people with celiac disease, which could be the first step towards new treatments.

Skills shortages and digitalization, trends in cardiology and oncology, future prospects in laboratory medicine, and healthy aging – these pressing topics are at the forefront of discussions at this year’s Medica Labmed Forum.

The microbiome – bacteria in the GI tract – is essential for digesting food and training the immune system. New studies explore how repeated antibiotic use can upset this delicate system.
Endoscopy is pivotal in diagnosing and managing ulcerative colitis. Recent technology advances allow for early cancer detection, precise disease assessment and targeted biopsies, improving diagnosis and monitoring. The following article takes a look at the latest advancements.
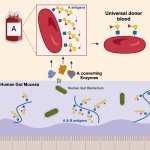
Donor blood is a scarce and valuable resource. Researchers aim to mitigrate this by using enzymes to remove specific sugars that make up the A and B antigens in the human ABO blood groups.

A specific subtype of a microbe commonly found in the mouth has been identified that is able to travel to the gut and grow within colorectal cancer tumors, driving cancer progression.

In a promising study, Canadian researchers have shown for the first time in mice that modifying intestinal flora before surgery could reduce postoperative complications in colorectal cancer patients.
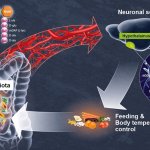
Hypothalamic neurons in an animal model directly detect variations in bacterial activity and adapt appetite and body temperature accordingly.
Common medications can accumulate in gut bacteria, a new study has found, altering bacterial function and potentially reducing the medications’ effectiveness. These interactions - seen for many drugs including those used to treat depression, diabetes, and asthma - could help researchers to better understand how drug effectiveness and side-effects differ between individuals. The study is…
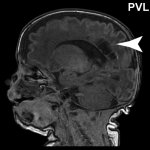
Extremely premature infants are at a high risk for brain damage. Researchers at the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna have now found possible targets for the early treatment of such damage outside the brain: Bacteria in the gut of premature infants may play a key role.
The variety and volume of bacteria in the gut, known as the microbiome, may influence the severity of Covid-19 as well as the magnitude of the immune system response to the infection, suggests research published online in the journal Gut. Imbalances in the make-up of the microbiome may also be implicated in persisting inflammatory symptoms, dubbed ‘long Covid’, the findings suggest. Covid-19…
A microbe found in the colon and commonly associated with the development of colitis and colon cancer also may play a role in the development of some breast cancers, according to new research from investigators with the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. Breast tissue cells exposed to this toxin retain a long-term memory, increasing the…

Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia. Still incurable, it directly affects nearly one million people in Europe, and indirectly millions of family members as well as society as a whole. In recent years, the scientific community has suspected that the gut microbiota plays a role in the development of the disease.
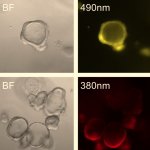
Researchers of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have cultured so-called intestinal organoids from human intestinal tissue, which is a common byproduct when performing bowel surgery.

Although the name may suggest otherwise, Parkinson's disease is not one but two diseases, starting either in the brain or in the intestines. Which explains why patients with Parkinson’s describe widely differing symptoms, and points towards personalised medicine as the way forward for people with Parkinson's disease. This is the conclusion of a study which has just been published in the leading…
Bacteria and other microorganisms in the digestive tract are linked with dozens of health conditions including high blood pressure, high blood lipids, and body mass index (BMI) according to research presented at ESC Congress 2020. “Our study indicates that microbiota might have an important role in maintaining health and could help us develop novel treatments,” said study author Dr. Hilde…
Disruption of gut bacteria by antibiotics soon after birth can affect the maturation of the immune system, say researchers at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. Even short, single antibiotic courses given to young animals can predispose them to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when they are older, according to their research. The study, published in Genome Medicine, provides further evidence…
An international team of researchers from the University of Zurich, the University Hospital Zurich, Heidelberg and Glasgow has identified a novel function for the cell death regulating protein MCL1: It is essential in protecting the intestine against cancer development – independent of bacterial-driven inflammation. These findings have implications for the use of MCL1 inhibitors, currently…
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and the Hebrew University in Jerusalem demonstrated in mice that intestinal bacteria reprogram DNA activity in cells of the gut mucosa and thus have a considerable impact on the development of the healthy gut.
In animals, a vaccine modifying the composition and function of the gut microbiota provides protection against the onset of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases and certain metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and obesity. This research was conducted by the team of Benoît Chassaing, Inserm researcher at Institut Cochin (Inserm/CNRS/Université de Paris), whose initial findings have been…

Prebiotics are currently a preferred treatment for certain metabolic disorders, as they can restore the balance of dysfunctional gut microbiota, and improve the body’s metabolism. However, these substances have to be used at high doses, which can result in patients experiencing bloating and flatulence. A research group led by Matteo Serino, Inserm researcher at the Digestive Health Research…

People who experience anxiety symptoms might be helped by taking steps to regulate the microorganisms in their gut using probiotic and non-probiotic food and supplements, suggests a review of studies published in the journal General Psychiatry. Anxiety symptoms are common in people with mental diseases and a variety of physical disorders, especially in disorders that are related to stress.…

Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found, in mice, that treatment with an antibiotic reduces the size of lesions caused by endometriosis. The researchers are planning a large, multicenter clinical trial to test the drug metronidazole in women who have the painful condition. The study is published online April 30 in the journal Human Reproduction.…

When the first antibiotics were discovered in the early 20th century, the rate of death from infectious diseases fell dramatically. But the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria as a result of antibiotic misuse is raising fears that by 2050, these same diseases will once again become the leading cause of death worldwide. In a bid to boost the arsenal available to tackle this threat,…

Cell stress in combination with an altered microbiota in the colon drives tumour growth. Previously, it was assumed that this combination only contributes to inflammatory intestinal diseases.
A Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine researcher has compiled evidence from more than 100 publications to show how obesity increases risk of 13 different cancers in young adults. The meta-analysis describes how obesity has shifted certain cancers to younger age groups, and intensified cellular mechanisms promoting the diseases. Cancer typically associated with older adults over 50…

Researchers have identified gut microbiota that interact with brain regions associated with mood and behavior. This may be the first time that behavioral and neurobiological differences associated with microbial composition in healthy humans have been identified.

Like spicy food? If so, you might live longer, say researchers at the Larner College of Medicine at the University of Vermont, who found that consumption of hot red chili peppers is associated with a 13 percent reduction in total mortality – primarily in deaths due to heart disease or stroke – in a large prospective study. The study was published recently in PLoS ONE.
Hospital-acquired Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is on the rise. Symptoms range from non-typical mild diarrhoea that can develop into pseudomembranous colitis up to a toxic megacolon, which often leads to death.

Colon cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in Germany. Prof. Dr. med. Sebastian Zeißig, group leader at the DFG Research Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD) - Cluster of Excellence at the TU Dresden and physician at the Department of Medicine I, University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden, has now shown a decisive role of gut bacteria in the regulation of intestinal…
Results from an international consensus project involving a multidisciplinary group of clinicians have been presented today at 26th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2016. A current lack of data on outcomes in patients with IBD who have CDI means that appropriate choice of treatment strategy can be unclear. The consensus examines the issues impacting…
The human body is inhabited by billions of symbiotic bacteria, carrying a diversity that is unique to each individual. The microbiota is involved in many mechanisms, including digestion, vitamin synthesis and host defense. It is well established that a loss of bacterial symbionts promotes the development of allergies. Scientists at Helmholtz Zentrum Munich, at the Technical University of Munich…
Research published in the open access journal Microbiome offers new evidence for the success of fecal microbial transplantation (FMT) in treating severe Clostridium difficile infection (CDI), a growing problem worldwide that leads to thousands of fatalities every year.
Allergic diseases represent a spectrum of health conditions and a worldwide burden in different populations. In the field of allergy and immunology the focus on prevention has become as important as effective disease management. Now for the first time there are guidelines that recommend proactive strategies for the prevention of allergic diseases. The World Allergy Organization (WAO) has…
The human gut literally teems with microorganisms from at least 1,000 different species that are increasingly considered to be a valuable resource for the prediction, aetiology and prognosis of disease. Due to continual contact with the environment, primarily via food, the gut is susceptible to infection when a virus, parasite or bacterium enters and disrupts normal gut microbiota (or flora).

Thermo Fisher Scientific, the world leader in serving science, today announced that the 2011 Oxoid W H Pierce Memorial Prize, which commemorates the late W H (Bill) Pierce, has been awarded to Dr. Brian Jones, senior lecturer at the University of Brighton, England. The award acknowledges Dr. Jones’ research into the human gut mobile metagenome, the mobile genetic elements (such as plasmids)…

454 Life Sciences, a Roche company, announced that a team of researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have characterized the human gut microbiome by sequencing the microbial communities of adult twins and their mothers with the Genome Sequencer FLX System.