Article • Personalised medicine
Gene-editing technologies: from lab to patient
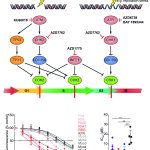
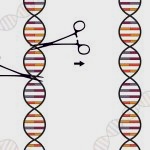
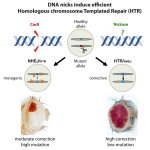
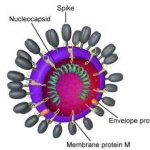
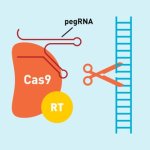
Gene-editing technologies show great promise for medical treatments and research, with the potential to cure thousands of genetic diseases. At the 2025 World Medical Innovation Forum in Boston, leading experts explored the possibilities and challenges of these rapidly advancing tools. The case of Baby KJ Muldoon – an infant treated with a personalised CRISPR therapy developed in just seven…