News • Nasopharyngeal cancer study
Covid vaccination improves effectiveness of cancer treatment
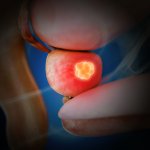
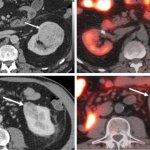
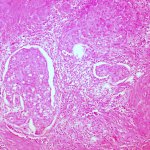
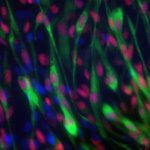
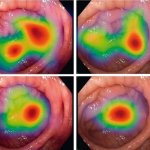
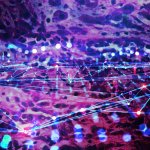
Until now, it was feared that vaccination against Covid-19 could reduce the success of treatment for patients with nasopharyngeal cancer. A recent study now gives the all-clear in this regard.