News • New insights on nosocomial pathogen
Research reveals ‘hidden movement’ of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
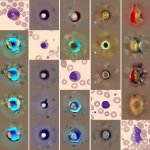
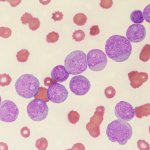
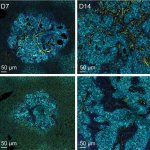
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a hospital-acquired bacterium that causes serious infections, can move from the lungs to the gut inside the same patient, raising the risk of sepsis, new research reveals.