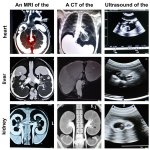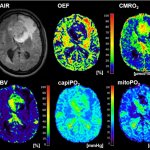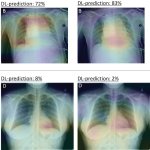
News • Deep learning in imaging
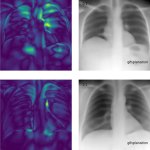
Earlier detection of diabetes through chest x-rays and AI
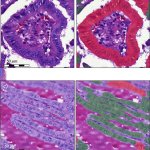
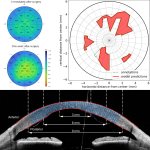
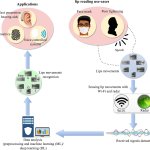
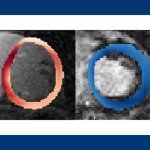
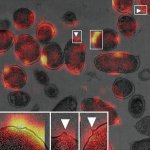
A new AI model finds that x-ray images collected during routine medical care can provide warning signs for diabetes, even in patients who don’t meet the guidelines for elevated risk.