News • Viral oncology
Kaposi Sarcoma: Answers to a longstanding enigma
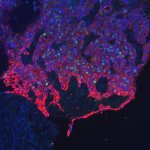
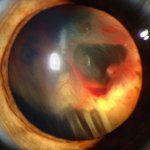
The oncogenic herpesvirus (HHV8 or KSHV) causes a cancer known as Kaposi’s Sarcoma. An international team of scientists led by the University of Helsinki has discovered key factors that control the genome maintenance and replication of a virus responsible for lymphatic vascular cancer. Kaposi Sarcoma (KS) is the most common cancer among Aids patients and it is often seen in sub Saharan and…