News • Oncology
Radio-wave therapy proves effective against liver cancer cells
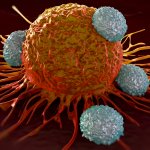
A new targeted therapy using non-thermal radio waves has been shown to block the growth of liver cancer cells anywhere in the body without damaging healthy cells, according to a study conducted by scientists at Wake Forest School of Medicine, part of Wake Forest Baptist Health.