News • Bioprinting in cancer
3D printing patient-specific tumours
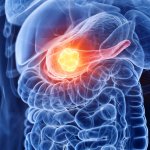
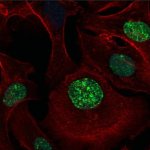
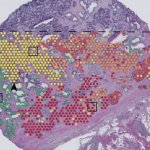
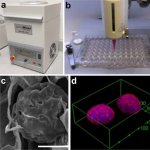
Bowel cancer patients could in future benefit from a new 3D bioprinting technology which would use their own cells to replicate the complex cellular environment of solid tumours in 3D models.