News • Intensive medicine
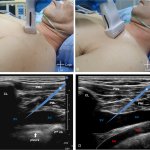
Ultrasound-guided cannulation for safer vein access
Performed inaccurately, cannulation of major veins is associated with complications like pneumothorax or artery puncture. Chinese researchers propose a new ultrasound-guided method for more accuracy.