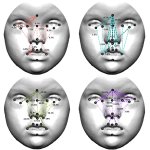
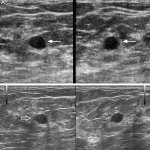
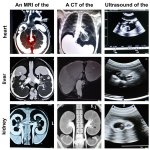
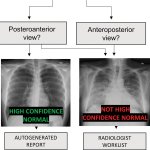
News • Patients' perception of AI avatars
Medical advice from ChatGPT: Can a bot's appearance stir bias?
Chatbots are increasingly becoming a part of health care around the world, but do they encourage bias? New research from the University of Colorado School of Medicine hints at this possibility.