Sponsored • Technology advances
AI-based diagnosis: New evidence for efficiency gains and better diagnostic accuracy
AI-based diagnosis is undoubtedly one of the most promising subjects when we talk about the future of radiology. However, some also see the usage critically and doubt whether the benefit outweighs the costs or rather the effort involved. Now, a couple of new studies indicate that most radiologists are open to using the technology and this for good reasons.
AI paves its way into routine in clinical practices
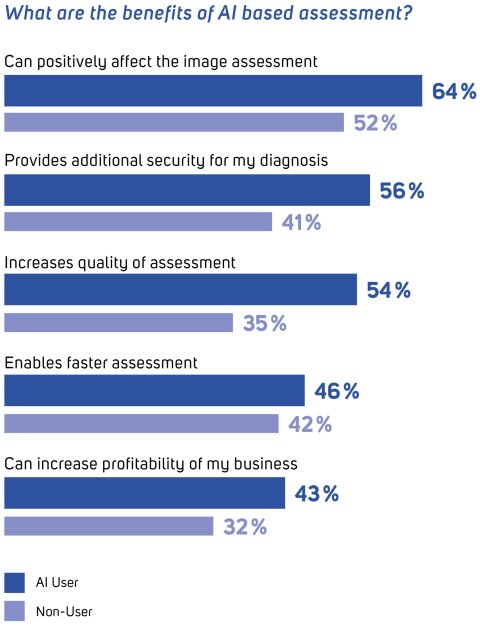
Since April 2022, a new usage study1 has been surveyed almost 200 radiologists in Europe about their attitude towards the use of AI-based diagnosis in radiology. The study is based on an independent and anonymous survey commissioned by mediaire and carried out by the market research institute Dialego. First results indicate that 30% of the participants are already using AI tools for diagnosis. Of those who have not yet used any such software, 64% show a positive attitude towards future utilization. Only 7% state that they would not consider using such a tool. However, image acquisition and diagnostics are the most common areas of application among users. Others play a rather subordinate role. The following criteria are mentioned as the main reasons for usage in the context of diagnosis.
- The software supports the diagnosis and serves as a quality control for own findings
- The software can help to ensure that pathological changes are not overlooked
- Working time can be shortened and efficiency improved

Reference: mediaire - AI usage study 2022
Area of application and indication are decisive factors
The qualitative added value of AI tools is particularly evident in areas where we traditionally observe high interrater variability, such as in the assessment of brain atrophy. Here, a good AI tool with precise volumetry, together with a robust normal model, can objectify findings very well. (Neuro)degenerative diseases can also be detected more quickly over time than the human eye can. The same applies to stroke diagnostics. Even when human performance is sufficient, it often takes a long time to complete complex tasks. This is the case, for example, when measuring brain tumors or when counting and measuring MS lesions. Also fluctuations in vigilance and a heterogeneous level of training sometimes results in overlooking findings - with all the consequences. Let's just think of the detection of pulmonary nodules, breast diagnostics or the detection of aneurysms. In all those cases AI tools can help to increase human performance.
Today’s tools are reliable and precise in daily routine
Reference: mediaire - AI usage study 2022
From the early days of AI-based diagnostics when precision of the tools was relatively poor, and it often took quite a long time before the findings were available, the tools came a long way. Current solutions show clear evidence that they are at least as precise and sometimes even more precise than a human expert reader. On top of that, they lead to significant time savings and reduce workload. A good example is mdbrain, a software suite for quantitative neuroimaging that provides applications that range from volumetric brain analysis down to the characterization of white matter lesions. Several independent studies which will be presented at ECR’22 clearly show how reliable, precise and efficient the tool works in clinical routine. Albert, J. et al.2 for example states, that mdbrain had a positive diagnostic impact in 118/128 AI-aided assessments. Among these cases, radiologist reported that mdbrain reinforced their original assessment” in 76 cases, “enabled a clearer diagnosis” in 25 cases and even “reported anomalies that could have been missed” in 7 cases.
Seamless integration is key for efficiency gains
In the same study Albert, J. et al. report that the tool can reduce assessment time up to 57% depending on type of the assessment2. However - to relieve their full potential in daily routine, the tools must integrate into the PACS or RIS without interrupting the workflow of the radiologist. With a state-of-the-art tool like mdbrain a report is usually created in 3 to 5 minutes. All this happens with one click or, if desired, fully automatically seamlessly in the PACS. In this way, the workflow of the radiologist is not interrupted, and no system change is necessary. To receive more information about recent publications or if you would like to test our products for free, meet us at the ECR or contact us via our website.
References:
1: https://ai-usage-study.eu/
2: J Albert et al. Real-life evaluation of the AI-based Neuroradiology Suite mdbrain. Presentation at ECR2022
13.07.2022